Author’s note: this proposal is the latest in a series on this blog aimed at a major Oregon Parks and Recreation Department (OPRD) effort underway to update the 1994 Gorge Parks Plan. OPRD staff will make key decisions on future trail projects for the Gorge over the next four months, so now is the time to weigh in! More information on how to get involved in this important work is included at the end of this article.
_________________
Mitchell Point is a rugged basalt spine that towers a thousand feet above the Columbia River, just five miles west of Hood River. This spectacular outcrop rises in the transition zone where the wet rainforests of the western Cascades meet dry Oregon white oak and Ponderosa pine country of the eastern slope in a unique jumble of ecosystems and geology.
The steep hike to Mitchell Point is described in this WyEast Blog article, and makes for an excellent year-round destination for hikers looking for something a bit less crowded (and a bit more rugged) than viewpoints like Angel’s Rest.
This article focuses on recent improvements to the Mitchell Point wayside and trailhead, and the potential to expand the trails at Mitchell Point to allow for better exploration of the unique landscapes found here, and a deeper appreciation of the colorful human history, as well.
Kudos on Recent Upgrades!

A short, new segment of the Historic Columbia River Highway State Trail leads to the refurbished Mitchell Point overlook
In 2012, the OPRD completed a major overhaul of the Mitchell Point wayside and overlook, with excellent results. Mitchell Point falls within the borders of the Vinzenz Lausmann and Seneca Fouts state parks, and has long served as a scenic wayside for highway travelers and as the trailhead for the Mitchell Point and Wygant trails.
The recent overhaul at Mitchell Point also acknowledges a new function for the trailhead: the Historic Columbia River Highway (HCRH) State Trail project will soon extend through the area, including a proposed tunnel through Mitchell Point, proper, that gives a nod to the iconic highway tunnel that once thrilled highway travelers here.

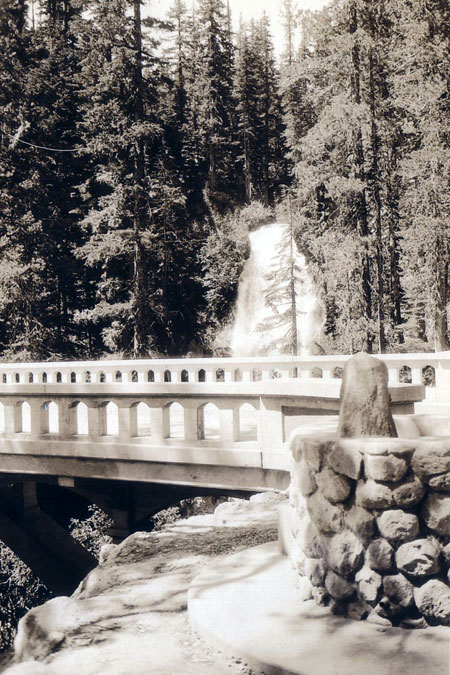
The restored overlook features a sweeping view of the Columbia Gorge and interpretive display on the iconic former Mitchell Point “Tunnel of Many Vistas”
In many ways, the original Mitchell Point Tunnel, with it’s famous “windows” carved in solid basalt, was the scenic and engineering highlight of the old highway. Sadly, the tunnel (along with much of the original highway) was destroyed to allow for freeway widening in 1966.

The original Mitchell Point Tunnel as it appeared around 1920. The tunnel was destroyed to make way for freeway widening in 1966
The recent improvements to the Mitchell Point wayside include a redesigned parking lot (complete with native landscaping, bus and bike parking) and a series of handsome stone walls in the Columbia River Highway style that frame the Columbia River overlook. Interpretive history displays are posted in two locations, describing the colorful human history of an area that has now largely reverted to back to nature.
The short walk to the river overlook also gives a glimpse of the planned extension of the HCRH State Trail. As seen in the photo below, the broad paved path is actually a section of the state trail where it approaches the overlook, then bends toward the sheer cliffs at the base of Mitchell Point, ending at a log fence (for now). The proposed tunnel will eventually cut through Mitchell Point here, with a short side-tunnel to a river viewpoint somewhere near the midpoint.

The new section of the HCRH State Trail points toward a planned bicycle and pedestrian tunnel through Mitchell Point
The improved Mitchell Point wayside also includes a new information kiosk and upgraded restrooms, making this a nearly full-service starting point for hikers — with the sole exception of running water, as none is available at the wayside.
A surprising glitch in the generally excellent attention to detail is the wayside overhaul is an ill-placed square of landscaping in the middle of the paved information kiosk mini-plaza (below). The native salal planted in this tiny square of soil are surely doomed to be trampled by visitors, but more concerning is the impact on accessibility for mobility impaired visitors attempting to avoid this unnecessary obstacle. Fortunately, it’s easily fixed with a few sacks of concrete – hopefully before it becomes a problem.
Traces of the rich human history of the area can be seen throughout the Mitchell Point area, and the pair of new interpretive displays help put a face on the early settlements and businesses that once operated here. The history of the Mitchell Point “Tunnel of Many Vistas” at the overlook is excellent, and told with well-known images of this famous structure. But the history of the Little Boy Ranch and its operators found near the parking area is especially welcome, as it helps repeat visitors understand the many traces of old structures and even trees and landscape plants that can still be found sprinkled through the forest.

The Little Boy Ranch motel and cabins at Mitchell Point in the 1930s. The buildings were razed as part of freeway construction in the early 1960s
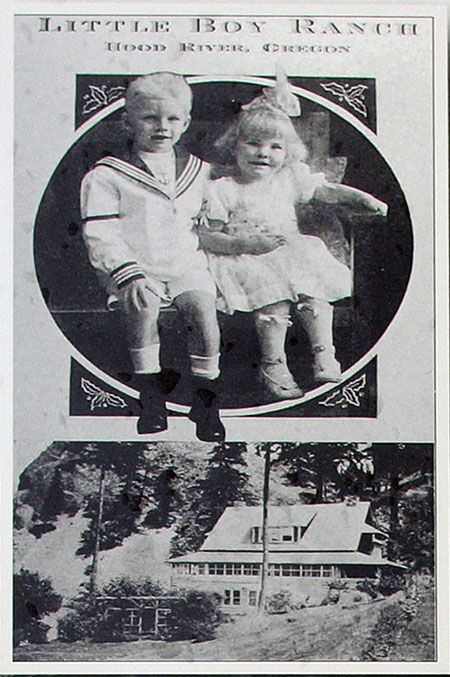

This 1920s Christmas card from Charles and Helena Parker’s Little Boy Ranch featured their children, Charles Jr. and Joan
While most of the historical traces at Mitchell Point are subtle and treasured, one is not: English ivy left over from the Little Boy Ranch days is rampant in several sections of the park, and unfortunately, the wayside upgrade didn’t include pulling ivy from the park. This is another oversight that can be easily corrected, as the ivy is mostly confined to the immediate wayside area, and is a good candidate for a volunteer public service projects.
Another surprising gap in the wayside and trailhead upgrade is the lack of signage for the Mitchell Point and Wygant trails that begin here. A few boulders and a bollard barricade have been installed at the old path leading toward the Mitchell Point Trail, but there is still no signage to help visitors navigate the trail (below).
Worse, the actual trail to Mitchell Point splits off the paved path as an obscure, unsigned boot path, while the paved route continues (confusingly) to a few picnicking sites (below). This oversight is easily remedied, though there is some question whether OPRD really views the Mitchell Point trail as one of its own, despite the growing use and popularity. Now is good time for the state parks to finally embrace this trail, starting with needed signage.

The formal Mitchell Point Trail is even more obscure, but this is an easily corrected oversight in the OPRD restoration project
The Wygant Trail fares somewhat better, with an existing HCRH-themed sign posted about 100 yards west of the Mitchell Point wayside, along a surviving segment of the old highway. But better signage at the wayside is needed to help hikers actually find this trail. This is another oversight that is relatively easy to correct, and in this case, could be incorporated into the planned improvements to the HCRH that are coming to this area.

A surviving segment of the old highway serves as the start of the Wygant Trail, though existing signage is obscure
Despite these oversights, the upgrade to the Mitchell Point wayside and trailhead are a big step forward, with excellent attention to detail and continuity with other recently improved parks and waysides in the Gorge. Kudos to the OPRD for their efforts!
The remainder of this article focuses on new trails that could be added to the park, building on existing facilities and the new HCRH State Trail with new hiking loops that explore the area.
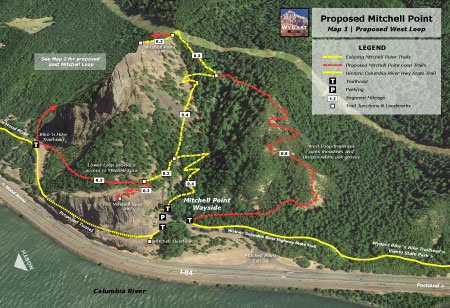
Proposal: West Loop Trail
The first leg of an expanded trail system would be a new route traversing a series of open slopes to the west of Mitchell Point, joining the existing Mitchell Point Trail just below the main summit ridge (see map below)
[click here to open a large map in a new window]
A highlight of this new 0.8 mile trail would be a close-up look at the stunted Oregon white oak groves that somehow survive on the dry, windy slopes here. Though not the western-most stand of oaks in the Gorge, this colony is among the most accessible, and the new trail would provide an opportunity for casual hikers to learn about this unique and fascinating ecosystem.
This new trail would also be built with a less demanding grade than the existing Mitchell Point Trail, giving less hardy hikers a more manageable option for reaching the summit.
Combined with the existing Mitchell Point Trail, the new would create a 2.6 mile loop for active hikers. Casual hikers and young families could make a shorter hike, with the beautiful oak stands and river views less than one-half mile from the trailhead as the main destination (perhaps with a couple of well-placed trailside benches).
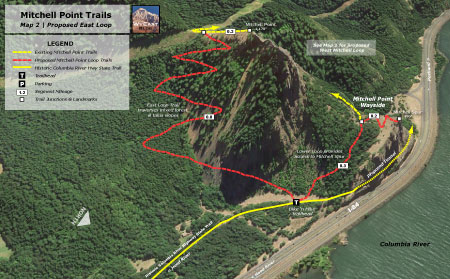
Proposal: East Loop & Mitchell Spur
The east slope of Mitchell Point is unknown territory, even to hikers familiar with the area. This part of the proposal includes a new trail connection along the east slope, from the crest of Mitchell Point to the planned HCRH State Trail, creating a loop hike via the proposed new HCRH tunnel (see map, below).
[click here to open a large map in a new window]
A lower loop would also be created with an extension of the existing boot path that leads to the foot of Mitchell Spur, the familiar basalt prow that towers over the highway at Mitchell Point. A formal side path would lead to the viewpoint atop the spur, providing another less strenuous alternative for casual hikers to the somewhat challenging Mitchell Point summit trail.
Combined with the existing Mitchell Point trail, the proposed East Loop would create a 3.6 mile hike, including stops at the summits of Mitchell Point and Mitchell Spur. Another option would be a loop using both the east and west trail proposals, a 3.8 mile round trip that would avoid the somewhat rugged talus section of the existing Mitchell Point trail altogether. Other loops from the Mitchell Point trailhead would also be possible, including the ability to follow the planned extension of the HCRH State Trail.
Yet another possibility that comes with the completion of the HCRH State Trail is the idea of a bike-and-hike trailhead for the proposed East Loop trail, where bicycle parking could be provided to allow cyclists to ride and park at the base of the trail. This concept has great potential for other trails that will eventually stub out at the completed HCRH State Trail — including the Wygant Trail in the Mitchell Point area.
What would it take?
The proposals in this article focus on relatively simple, affordable trail projects. Each of the proposed trail segments build on existing trailhead facilities and planned HCRH improvements in the area, while providing a significantly expanded series of hiking opportunities.
The proposals also lend themselves to volunteer construction, as the easy access from Portland and Hood River would allow public agencies and trail advocates in the region to easily organize volunteer crews to clear and build trails incrementally.
Most importantly, the OPRD is now in the process of updating its 1994 master plan for the Columbia Gorge, and it’s a crucial opportunity to bring new trail ideas into the plan! The OPRD recognizes the demand for new trails in the area, and is actively seeking ideas for projects that are both affordable and ecologically sustainable. The proposals in this article meet both tests, and ought to be included in the updated plan.
What You Can Do!
First, take a look at the Gorge Parks Plan website — our state recreation planners have done an exceptional job scoping the state of our Gorge parks as a starting point for updating the 1994 plan.
Next, weigh in on why new trails are important in the Gorge — and here are some of the proposals posted in this blog as a starting point:
Finally, consider signing up as a subscriber to the Gorge Parks Plan blog to stay informed. A surprisingly small number of dedicated citizens have been involved thus far in this public process, so you have an opportunity to make a real impact! More information on the Gorge planning effort to come in this blog, as well.
And as always, thanks for doing your part to advocate for the Gorge!