First snow of autumn 2018 on Mount Hood as seen from Dufur Mill Road
Last November marked 10 years since I started the WyEast Blog, way back in 2008. It was a pretty hopeful year, as you may recall, followed by some very progressive reforms for how our public lands are managed. And my, how things can change — elections do have consequences! So, as always, the work continues as we weather another round of political attacks on our hard-fought protections for public lands.
Much has changed in WyEast country over the past 10 years, too, but certainly not my commitment to a better future for Mount Hood and the Columbia River Gorge. I’m frequently asked “do you reallythink Mount Hood will become a national park?” and my response is always the same, “a little more every day!”Why? Because despite the currently bleak situation in Washington D.C., we’re (finally) witnessing the start to a changing of the guard in generational leadership at all levels of our society. The Millennials are here!

Author on my last visit to Eagle Creek, about a year before the September 2017 fire
What will history say about the Baby Boomers as they (reluctantly) hand over the reins to a younger generation? For all they have given us in their epic contributions to art and culture, they have also been surprisingly awful when it comes to conservation, woefully lacking in both courage and imagination. It’s true the Millennials are overdue in taking the reins, but since twice delivering the first African American to the U.S. presidency (a man who the Boomers voted overwhelmingly against, history shall note), they have steadily expanded their presence on the local, state and national political scenes. The 2016 elections represented the beginning of what will become a tidal wave in coming years, too.
By wide margins, Millennials are genuinely committed to conservation and sustainability, more balanced in their personal lives in how they manage ambition and status, and much less materialistic and consumptive than their elders. The numbers prove this. And thus my confidence that the Millennials’ turn at governance can (and will) return us to the bold conservation legacy of past eras and previous generations of leadership. The pendulum will swing, once again, and I believe that expanding our national park system will be part of that renaissance.
In the beginning…
Ten years ago, I started this blog with a rather obscure look at a couple of dead trees at a favorite roadside viewpoint of mine, along Dufur Mill Road. Here’s what that spot used to look like:

The two snags featured in the very first article on this blog… but what about the big fir on the right?
Sometime that year, both snags on the left side of the photo were felled, possibly for firewood, a common activity in that area. At the time I was dismayed at the senseless loss of a couple of valauble and (to me) beautiful snags. Mount Hood’s old ghost trees are essential for wildlife and forest health, after all! And thus, my first article began what would become many looks at the lesser-known and under-appreciated corners of WyEast country, all in celebration of our magical mountain and gorge!
Today, the view from this spot on Dufur Mill Road is still much the same, minus the old snags. Here’s what it looked like a couple of weeks ago (below), where you can pick out individual trees in the background that appear much the same. The large Douglas fir on the right side of the original photo still stands, too, but what about the apparent change in height of this tree between the above and below photos?

Today the two snags are long gone, but the big Douglas fir is still standing
Yes, the old fir did grow, but not by that much. It turns out that in the 10 years since the original photo was taken, a young Douglas fir has grown from just a few feet tall to nearly 20 feet — blocking the original view! Here’s what today’s scene looks like as viewed from the exact spot as the 2008 photo:

The only true constant in the forest… is change!
The changes in this favorite spot of mine are a good metaphor for so many places on Mount Hood and in the Gorge over the past ten years, where the only constant is change. This article explores some of the changes, plus a rundown of the most read and least read articles on the blog. Hope you enjoy the look back!
The Articles
Including this retrospective, I’ve posted 184 articles on the blog since November 2008, ranging from the incredibly obscure (my favorite!) to the surprisingly popular.
In the first five years, visitors grew gradually to a couple thousand annually, then abruptly jumped to 30,000 in 2013 and 60,000 in 2014! Since then, visitors have hovered between 70,000 and 90,000 annually. A decent share also click through to the Mount Hood National Park Campaign website, and who knows? One of those visitors might be the future congresswoman or senator who introduces a bill to make Mount Hood and the Gorge a national park! That’s the goal of an “idea campaign”, after all — and why I started the blog.
But blog metrics don’t really tell the full story, as a select few posts have been the major drivers in visits over the years. These posts continue to pop up each week in the blog stats, years after they were first published.
At the top of that list is an article debunking the many persistent myths about ticks that continue to circulate among the hiking community. I published “Ticks! Ticks! (10 Common Myths” in April 2013, and it’s the main reason for the big jump in traffic that year that has since continued. The article now has 173,000 views and counting — and that’s great news, as ticks present a growing health risk in the Gorge now that Lyme disease has spread to our region.

Nobody likes ticks… but people do like this article!
Right behind ticks in our apparent collective anxiety is poison oak, and a companion piece called “10 Common Poison Oak Myths” is thus the second most read article on the blog. A lot of bad information circulates online among hikers on both the risks and treatment for poison oak exposure. This article was posted in 2012, before the tick article, but caught fire after the piece on ticks began to drive search engines toward the blog. Today, the poison oak article has had 78,000 visitors and shows up every week in blog stats.

I’d been itching to write the sequel to this one…
The 2017 Eagle Creek Fire kicked off a series of articles covering the aftermath of the fire. The first article featured some of the earliest views into the burn as seen from the Washington side of the Gorge, just after the smoke had cleared. This article was widely shared in social media, with 23,000 views and counting.

The first look into the smoky aftermath…
Later articles spotlighting the burn were based on State of Oregon aerial reconnaissance photos that provided exceptional detail of the devastation at iconic places in the Gorge and the nearly immediate signs of recovery that was already underway. One of these revealed a massive cliff collapse at Punch Bowl Falls in early 2018, just a few months after the fire.

Perhaps more shocking than the Eagle Creek Fire, itself, were the dual cliff collapses at Metlako Falls and Punchbowl Falls on Eagle Creek.
We will never know if the cliff collapse resulted from the effects of the fire, but when the State of Oregon aerial surveys revealed the collapse, it came as a shock to anyone who knew this spot. More than 25,000 readers have viewed the article and it continues to be visited regularly.
While it’s great to see a big response to an article, truth be told, my favorite posts are among the least read. This describes mostof the posts on the blog, of course!
One of these lesser-read pieces was in 2010, when I posted a proposal to restore Warren Falls, a virtually unknown spot near Starvation Creek that had been brutally altered by Highway Department engineers in the 1930s. I had long been saddened to see how this beautiful spot had been manhandled by the same Highway Department that had gracefully navigated other waterfalls in the Gorge with beautiful bridges, viaducts and overlooks, and hoped that ODOT might incorporate restoration of the falls into a major effort to reconnect the original Historic Columbia River Highway.

This became a bit of a crusade for a few years, including a featured spot on OPB’s Oregon Field Guide, but in the end, ODOT wasn’t interested in owning up to their crime against nature (and as I pointed out in one of the follow-up articles, the diversion was a clear violation of state statute, too!). Score another one for the highway builders, but I remain hopeful that someday we will undo this travesty.

Warren Falls comes (briefly) alive in 2014!
In the meantime, a vestige of the original falls appears a few times each winter when ODOT’s diversion dam and bypass tunnel are overwhelmed by high runoff, bringing Warren Falls back to life, if only briefly.
And while ODOT once again turned its back on Warren Creek, Mother Nature may bring her wrath upon the diversion structures in the aftermath of the Eagle Creek Fire. Ironically, the original project was in response to Warren Creek carrying heavy rock and wood debris onto the old highway following an early 1900s burn in the upper canyon Eighty years later, the upper canyon has burned again, and another cycle of heavy debris flows is likely in coming years. She does bat last, after all…
In happier ODOT news, an August 2012 article proposing a “Boot Loop” transit service around the mountain and through the gorge seemed far-fetched at the time, but ODOT has since operated transit in the west end of the Gorge and helped fund transit to Timberline Lodge. Currently, a “round the mountain” transit study is underway to explore the potential for completing the loop. That’s great news!

Not such a goofy idea after all..?
The Gorge Express and Mount Hood Express bus lines are general purpose, too, whereas the “Boot Loop” idea was more narrowly aimed at recreation. The broader transit service we’re now seeing on the ground is far better, providing essential service to places where basic transit connections were long overdue. Kudos to ODOT for moving beyond their highway roots and bringing much-needed transportation alternatives to the mountain and gorge!
10 years of Big Changes
Mount Hood and the Columbia River Gorge have seen some epic changes over the past 10 years, perhaps most notably the Dollar Lake Fire on Mount Hood’s north slope in 2012 and the Eagle Creek Fire that burned much of the Oregon side of the Gorge in 2017. But there were many other significant changes, too, albeit somewhat overshadowed by the big fire events. The following are a few “then and now” highlights of these notable changes in WyEast country over the past ten years.
Global warming? Absolutely. Despite the frustrating, science-defying (and completely cynical) state of denial coming from the White House and Republican Party, bright red warning flags are showing up all around us, including on Mount Hood. As the photo pair below shows, the Eliot Glacier continues to recede at an alarming rate, as do the rest of Mount Hood’s twelve glaciers. I’ve marked a couple of prominent rock outcrops adjacent to the lower Eliot Galcier icefall to show how the “firn” line has retreated. The firn line is the point in a moving glacier that marks equilibrium, with the glacier is accumulating ice above the line and losing ice (melting) where it flows below the firn line.

Blue ice still spilled over the lower Eliot Glacier icefall in 2008
As the photos show, the lower icefall (just above and left of the outcrop marked “A”) is notably smaller and darker, with debris carried within the glacier now exposed by melting at this level due to the rising firn line. Both photos were taken in late summer, when summer melting was at its peak.

Global warming is rapidly changing the once-mighty Eliot Glacier
The once-permanent snowfields on the margins of the glacier are also noticeably smaller and seem doomed in the near future. Permanent snowfields are the most vulnerable ice features on the mountain and a good visual indicator of the speed in which global warming is melting our glaciers.
While future generations may forgive us for failing to actually slow or stop global warming, they surely will never forgive us for willful denial of its existence as a human-caused crisis of our own making. Let’s hope we can make up some lost ground in the near future, with the Millennial generation finally taking charge.
The changes to the Eliot Glacier are also being felt downstream, no more so than in the upper reaches of the Eliot Branch canyon, where a more volatile glacial outflow is rapidly carving into the once glacier-covered valley floor, constantly changing the landscape. In 2006, the stream flooded once again, greatly deepening the canyon and making it unsafe to cross for hikers on the Timberline Trail. This situation languished for nine years, with many hikers choosing to scale the crumbling canyon wall (shown below) with the aid of a worn rope anchored to a boulder!

The ever-deepening canyon on the upper reaches of the Eliot Branch
This blog played a small part in helping the Forest Service move forward with a new crossing of the Eliot Branch when a ranger from the Hood River District read this 2014 article and reached out to discuss options for a new, downstream crossing. Along the way, I updated the map from the blog article to align with Forest Service and Trailkeepers of Oregon (TKO) plans for the restored crossing, and it even made the cover of a local newspaper in Hood River! (…okay, so it’s an advertising tabloid…!)

Not exactly the New York Times, but I’ll take it!
The newly reconnected trail drops steadily from Cloud Cap Inn to a section of the raging Eliot Branch that has (somewhat) stabilized, and can be reasonably crossed in the summer months. Though there are no immediate plans for a trail bridge here, the Forest Service moved large boulders in the stream to serve as stepping stones, hopefully making the crossing a bit safer for hikers. The restored trail opened in 2017.

The newly constructed Timberline Trail just above the Eliot Crossing (photo: USFS)
Moving down to the Hood River Valley, the iconic view of Mount Hood from this field along Laurance Lake Road (below) looks much the same today as it did in 2008, albeit with some logging on private land in the distance. What you can’t see in the 2008 view is that it was captured just a year after voters approved Measure 49, which reversed 2004’s deceptive Measure 37. This earlier measure would have almost certainly brought resort development and luxury McMansions to the Hood River Valley.

The timeless view of Mount Hood from Laurance Lake Road

…still pretty much the same ten years later!
Even better, this farm has since come under the ownership of a member of the Parkdale Valley Land Trust, and is now even more likely to remain unchanged for the foreseeable future. Which, in turn, means that a spot that hasn’t change since the 1950s (below) might look much the same in the 2050s. That’s a great legacy being carried forward to future generations.

Maybe past really can be prologue..? (photo: State Archives)
Here’s another view of the Parkdale area in the Upper Hood River Valley from Middle Mountain, a mostly county-owned forested ridge that separates the upper and lower valleys. From this spot, the most notable change is a silver band of ghost trees marking the 2012 Dollar Lake burn, clearly visible along the northern shoulders of the mountain.

The upper Hood River Valley ten years ago…

…and earlier last year…
The Dollar Lake Fire was the third in rapid succession (following the Bluegrass Fire in 2006 and Gnarl Ridge Fire in 2008) to burn the slopes of Mount Hood. As jarring as the changes may be, these new burns provide a front-row seat to the rapidly recovering forest, a timeless and essential cycle that has been disrupted by the Forest Service policy of aggressive fire suppression over the past century. State and federal land agencies have only just begun to rethink their approach to fire moving forward, a change in culture that will take many years to fully achieve, especially in the era of climate change.

Huckleberries sprouting from the base of a burned snag in the Dollar Lake Burn
One unexpected benefit of the fires on Mount Hood was preparing those (like me) who love the mountain and gorge for the devastating Eagle Creek Fire that raged through the western Columbia River Gorge in September 2017. The Mount Hood fires helped many who understood the abstract benefit of forest fires come to grips with the emotional reality of seeing a favorite place changed, and begin to appreciate the stark beauty in the burned landscape and witness the unfolding forest rebirth.
For the past year, thousands of volunteers with organizations like Trailkeepers of Oregon (TKO) have been working with the Forest Service and Oregon State Parks to begin digging out miles of burned trails in the gorge. Last November, the Forest Service officially opened the first of these cleared trails, including the iconic Larch Mountain Trail that follows Multnomah Creek, giving hikers their first look at the changed landscape, and a chance to expand their own understanding and acceptance of fire in our forests.
Earlier last year, I joined TKO crews to work on the trail and capture photos of familiar scenes as they now appear, after the fire. This set shows Weisendanger Falls from the same spot before and after the fire:

Weisendanger Falls on Multnomah Creek ten years ago…

…and in spring 2018, after the Eagle Creek Fire swept through
While the area below Weisendanger Falls shows signs of the fire — notably , more logs in the creek — this photo pair shows the extent of the burn above the falls, where the forest was more substantially impacted:

Weisendanger Falls before…

…and after the fire, in spring 2018
Similar scenes can be found throughout the Eagle Creek Burn, where the fire generally left a beneficial “mosaic” pattern, with heavily burned areas mixed with largely intact forest. These areas are expected to recover quickly, with healthy patches of surviving forest helping adjacent burned areas recover by reseeding, providing cover for wildlife and creating shade. But there are exceptions, especially Oneonta canyon, where the burn was especially catastrophic. The recovery in these places will span decades.
* * * * *
Thus far in this 10-year retrospective article, the focus has been on big changes brought by nature (albeit with an assist from man), but there have been plenty of changes brought by humans over the past ten years, too — both good and bad.
Let’s start with the bad (and ugly). Tragically, corporate timber behemoth Weyerhaeuser became the major private land owner in the West Fork Hood River valley over the past decade, taking ownership of private forests that had long been held by Longview Fibre (and then briefly by a Canadian equity trader). Though Longview Fibre had greatly accelerated logging in the 2000s, Weyerhauser has ramped up the destruction and embarked on a complete liquidation of the forests along a West Fork. Their purported “sustainability” mission is laughable in the modern area of chasing stock prices with massive, unsustainable clear cutting.
This scene is along the spectacular West Fork canyon, just above the Lake Branch confluence. It’s a crime against nature that any private entity should own land of this scenic and ecologic value, and Weyerhauser’s recent “stewardship” is proof:
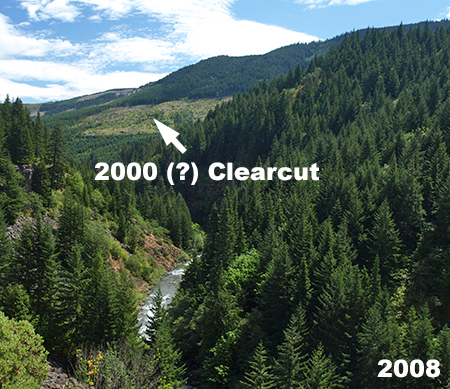
Weyerhauser didn’t own it yet, but the assault had begun…

…but Weyerhauser greatly accelerated the deforestation of the West Fork
Not seen in these photos are the miles of shoddy logging roads cut into steep slopes in order to haul out the logs and the millions of gallons of liquid herbicide sprayed on the slopes of the West Fork canyon to kill whatever vegetation managed to survive the logging show. Modern corporate logging is about exterminating native forests and replacing them with hybridized tree farms, make no mistake about it.
Some of the more appalling Weyerhaeuser logging practices are on display along the canyon section of the West Fork, where the river cascades beneath towering basalt cliffs where the scenery would merit park status anywhere else in the country. In this spot, a healthy forest directly adjacent to the canyon wall was cut in 2016 and sprayed with herbicides in 2017, with no regard to the river corridor, directly below:

A forested bluff above the West Fork canyon ten years ago…

…and in 2018 after Weyerhaeuser had “sustainably managed” it…
While it’s tough to see healthy forests cut on such a reckless scale, it’s also possible that Weyerhaeuser’s new lust for quick profits over sustainability could tempt the company to sell their cut over lands to the public in the interest of protecting the West Fork valley over the long term. After all, it will take decades for these forests to recover, and Weyerhaeuser seems to have lost patience with timelines on that scale. The sooner we can reclaim these precious lands for the public, the better.Watch for a future blog proposal on that subject!
On to more positive developments! 2018 also marked the grand re-opening of the Old Vista Ridge Trail, a wonderful “lost” trail that winds north from the Vista Ridge Trailhead to a dramatic view of Mount Hood’s north side from a rocky spur known as Owl Point. The trail was unofficially reopened in 2007 by volunteers from the Oregon Hiker’s forum and maintained ever since, a project that led to the formation of Trailkeepers of Oregon (TKO).

User-made trail signs ten years ago…
Over that time, it became clear that the trail needed to be officially recognized by the Forest Service in order to be properly maintained over the long haul. After much discussion, the agency signed an agreement with TKO in 2017 to adopt the trail, caring for it in perpetuity.
The grand re-opening was originally planned for the fall of 2017, but the Eagle Creek Fire intervened, with much of the north side of Mount Hood closed to the public for fear of the fire moving south into the West Fork valley and toward the mountain.

…replaced with official Forest Service signs last summer!
In July of last year, the rescheduled re-opening finally happened, with an official “cutting of the survey tape” with loppers and a log saw by TKO’s executive director Steve Kruger and Hood River District Ranger Janeen Tervo. A celebratory stewardship day followed on the trail, and so began a new era for this wonderful trail. TKO and the Forest Service are planning other new trails in the area, so hopefully Old Vista Ridge marks the beginning of a trail renaissance on Mount Hood.

Making it official!

TKO volunteers celebrate at Owl Point on dedication day
The Old Vista Ridge Trail is snowed in for the winter, now, but you can visit most years from mid-June through October to admire the view and the new, official trail signs! Read more about the trail in the Oregon Hikers Field Guide.
Not far from Old Vista Ridge, another “lost” spot was saved in 2015 when the Western Rivers Conservancy rescued it from Weyerhauser through a direct land purchase. Western Rivers later sold the land to Hood River County at a deep discount, thanks to a Oregon Parks and Recreation Grant, which in turn was submitted on behalf of the county by another non-profit, Thrive Hood River (then called the Hood River Valley Residents Committee). Trailkeepers of Oregon (TKO) was in the mix, too, offering to build a trail system in the new county park as part of matching contribution toward the state grant.

This sign marks a new era for Punchbowl Falls
Sound complicated? It was! But the good news today is that most of the trails envisioned in the original park concept are now complete, and can be explored today. There are still a few finishing touches (notably, trail signs, which are currently in progress thanks to a Hood River scout troop — this is very much a DIY park!), but the main pieces to this new nature park are in place for all to enjoy.
The main focus of the new park is dramatic Punchbowl Falls, a powerful waterfall on the West Fork of the Hood River that has carved an enormous amphitheater from solid basalt. The area just below the falls is also reserved for tribal fishing, a native tradition here that spans millennia and continues to plays a central cultural and economic role for local tribes.

The massive basalt amphitheater at Punchbowl Falls
When the new trail network at Punchbowl Falls Park was first scouted in 2016, great care was taken to respect fishing paths used by the tribes to access the falls, while also providing a way for park visitors to enjoy the many views in this beautiful canyon. Another goal was to consolidate the confusing maze of user trails in the area. All of the work was completed by volunteers from 2016 through last fall.

Volunteers scouting the proposed trail network

Building the Dogwood Trail in 2017

Building the lower Yew Trail last year
The newest trail was completed last November, and follows the West Fork to the confluence of the East and West Forks of the Hood River, another popular feature in the park. Though the trails won’t be signed until early next year, they’re easy to follow and explore, and the park is especially peaceful in winter if you’re looking for a quiet walk in the forest. You can read about the hike here in the Oregon Hikers Field Guide.

The completed Yew Trail along the West Fork this fall
The new Punchbowl Falls Park spans roughly two miles of river, forever protecting land that had been left to the mercy of private timber corporations for more than a century. As if to underscore this point, Weyerhauser promptly logged off an entire hillside that rises directly above the new park before the site had even been transferred to county ownership. Thankfully, they spared the Punchbowl property from a similar fate before selling it to Western Rivers.

Thanks for the new view from Punchbowl Bridge, Weyerhauser…
Another big change over the past decade came to perhaps the most popular trail on Mount Hood, the venerable Mirror Lake trail, located near Government Camp. For nearly a century, this beloved trail to a small mountain lake was a “first hike” to thousands visiting the mountain for the first time, including me!

One last snowshoe trip to Mirror Lake before ODOT closed winter access
A series of early articles in this blog focused on an ill-conceived ODOT project to widen Highway 26 in the Laurel Hill section, just west of Government Camp. The original Mirror Lake trailhead was part of the collateral damage of this now-completed road widening project. Even before the widening project, ODOT began closing the old trailhead during the winter months, cutting off access to legions of snowshoers and skiers who had used it for years. Later, the widening project finished the job permanently, and the old trailhead is now closed – including removal of the old footbridge over Camp Creek.

Dogged snowshoers were not easily deterred by the winter closure in 2010
While ODOT focused on highway widening, a little known federal highway agency known as the Federal Lands Division worked with the Forest Service to design and build a new Mirror Lake trailhead at the west end of the Mount Hood Ski Bowl parking lot. This arm of the Federal Highway Administration also oversaw the recent replacement of the White River Bridge and restoration of the Historic Sahalie Falls Bridge, near Hood River Meadows. The new Mirror Lake Trailhead opened just a few weeks ago, and was immediately filled to overflowing with visitors.

The new Mirror Lake Trailhead

The new trailhead features toilets and handsome stone work
I’ll post a proper review of the new trailhead and trail once the snow melts this year, but perhaps the best outcome is restored winter access to the Mirror Lake area. Another important element of the project is a barrier-free design from the trailhead to a new footbridge over Camp Creek, a much-needed addition to the very limited number of accessible trails in the Mount Hood area.

Paved, barrier-free section of the new Mirror Lake Trail
One of the more profound changes of the past ten years came when President Obama signed a major wilderness bill into law in 2009 that greatly expanded wilderness protection in the Gorge and around Mount Hood. That law protected several small areas on the margins of existing wilderness that had been left out of earlier legislation. One such area is along the western margins of the lightly visited Salmon Huckleberry Wilderness, which ironically is the closest designated wilderness to the Portland metropolitan area. The expanded boundary incorporates forested slopes of Wildcat Mountain and McIntyre Ridge that had long been tempting targets for Forest Service timber sales.
At about that time in the late 2000s, the Bureau of Land Management abruptly closed a northern access point to the Salmon-Huckleberry Wilderness, where an old logging spur provided access to the McIntyre Ridge Trail. Hikers soon discovered a new way to access McIntyre Ridge from another logging spur located on Forest Service land, which in turn led to an ancient roadbed from a long-ago era when a forest lookout tower stood on Wildcat Mountain.

This section of the McIntyre Ridge Trail follows a former lookout access road
The Forest Service still has not embraced the “New McIntyre Trailhead”, as it is known to hikers, but this unofficial trailhead has restored public access to this newly protected corner of the Salmon Huckleberry Wilderness. More importantly, this is an area where “eyes on the forest” are especially important, as the Wildcat Mountain area has a long history of lawlessness and abuse from shooters, dumpers and 4-wheelers.

Blaze along the McIntyre Ridge Trail

Shooters can’t seem to resist destroying public property… and anything else they can shoot
The good news is that hikers have continued to use the McIntyre Ridge trail over the ensuing years, though there are still too many reports of illegal activity. Just last summer, a local hiker came across a pair of pickups that had driven at least a mile into the Salmon Huckleberry Wilderness along McIntyre Ridge and set up a camp in the middle of the trail! Worse, off-roaders have cut completely new roads into the wilderness on the margins of the Salmon Huckleberry, especially in this area. These are federal crimes, of course, though Forest Service resources for enforcing the law are minimal.

Rogue off-roaders well inside the Salmon Huckleberry Wilderness earlier this year (photo: Walrus)
Fortunately, public land law-breakers are well aware of their illegal behavior and tend to shy away from busy recreation areas. Therefore, my hope is that the Forest Service will eventually recognize and champion the New McIntyre trailhead as for protecting the wilderness through “eyes on the forest”. More to come in future articles on this little corner of Mount Hood country..
And the next 10 years..?
Looking at the many profound changes in the Gorge and around Mount Hood over the past ten years, it’s easy to feel a bit overwhelmed and discouraged by the pace and scale of change. The 2017 Eagle Creek Fire was especially traumatic for so many who love the Gorge. But the changes are also a reminder of the ongoing need for vigilance in protecting these special places and the role we all have to continue moving Mount Hood and the Gorge toward a new vision of restoration and renewal and away from our exploitive, often destructive past.
I’m optimistic that we’ll continue making progress in coming years, just as we have over the past decade that I’ve documented with this blog. I plan to continue posting articles here to track the changes and make regular deep dives into the lesser known corners of the Gorge and Mount Hood. And I’ll also dream a bit about how we might better care for these places that we all love while making our public lands more accessible to everyone.

Hiking with Mom on Park Ridge in my formative years!
Over the course of the past ten years, I’ve tried to post at least once per month, but you might have noticed that I haven’t quite kept that pace over the past year or two. That’s largely due to the fact that my elderly folks have suddenly needed more help as they both struggled with failing health. In September, my mom passed away after a long and cruel struggle with memory disease, so we’ve now shifted to supporting my 89-year old dad as he adjusts to suddenly living alone after 68 years of marriage.
While sorting through family memories of Mom, I came across a photo (above) from a family backpack through the Mount Jefferson Wilderness, way back in 1974 when I was 12 years old. I was already an experienced hiker and backpacker at that point in my life, thanks to the love of the outdoors my Iowan parents shared in their beloved, adopted Pacific Northwest.

Me (standing on the rock, of course!) with my mom and sister on a Timberline Trail backpack in 1976
That’s a precious gift my folks gave to me and I’m thankful every day for my good fortune to have been raised with boots on my feet and a pack on my back! Too many in our spectacular corner of the world take our public lands for granted, and barely make the time or effort to explore them, often because they don’t really know how to. That’s another motivation for the blog and the Mount Hood National Park “idea campaign”. Our public lands are a gift for all of us, and I’ll also continue to post articles that celebrate this legacy and provide tips for how to explore the lesser-known corners of WyEast country.

Older, grayer but ready for another 10 years of celebrating WyEast!
Well, that’s probably more than enough for this retrospective article. But if you’re read this far, thank you for taking the time to visit the blog and especially those who’ve reached out with a comment or e-mail over the years. Much appreciated! I’ve got a bunch of articles and a few surprises in the works heading into 2019, and I’m looking forward to another 10 years!
I hope to see you here along the way — and on the trail, too!
_________________
Tom Kloster • January 2019