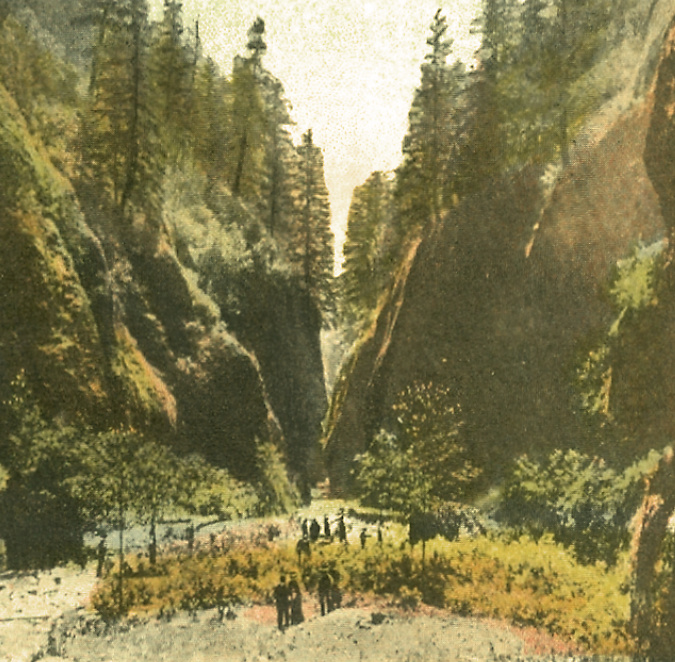
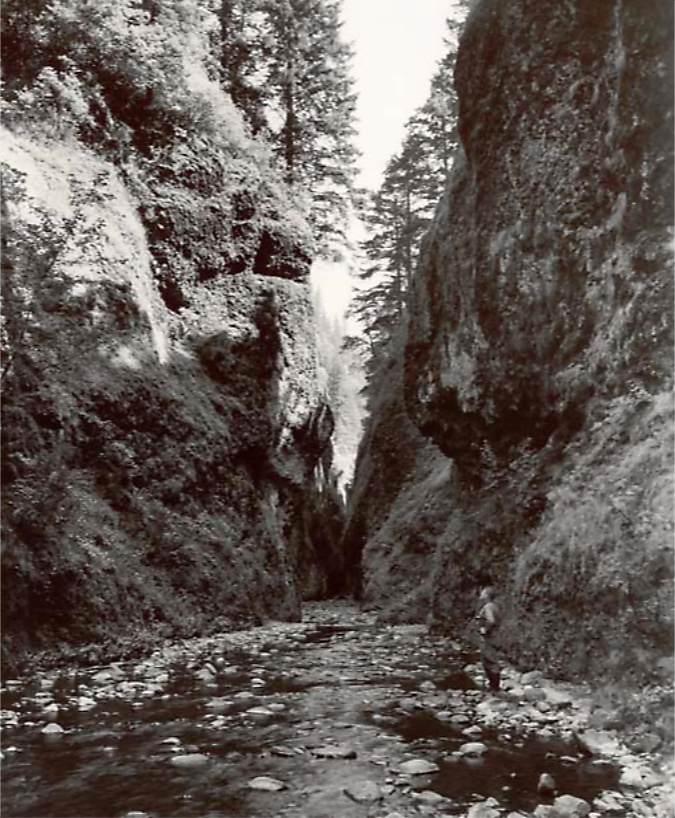
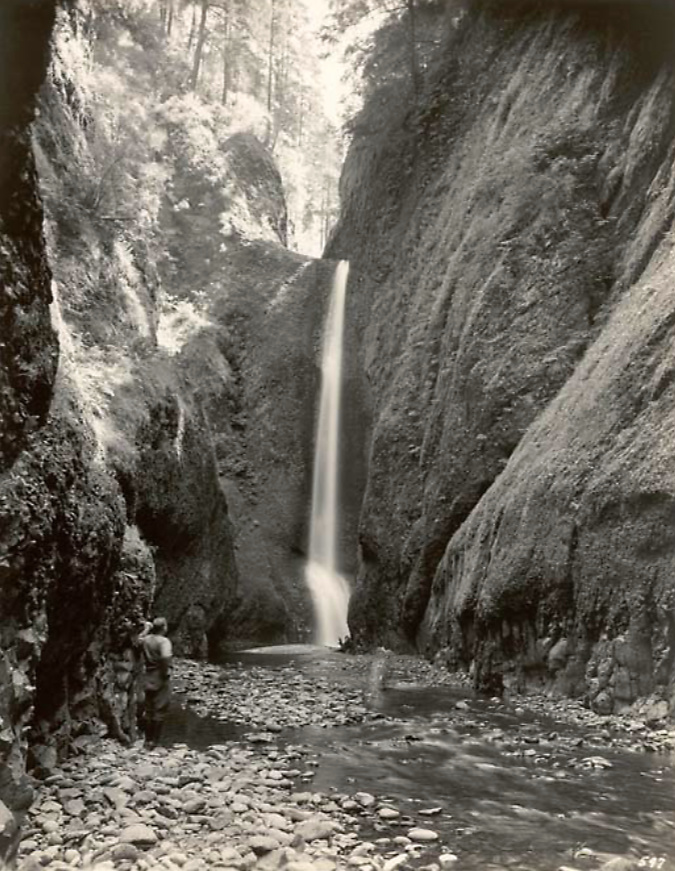
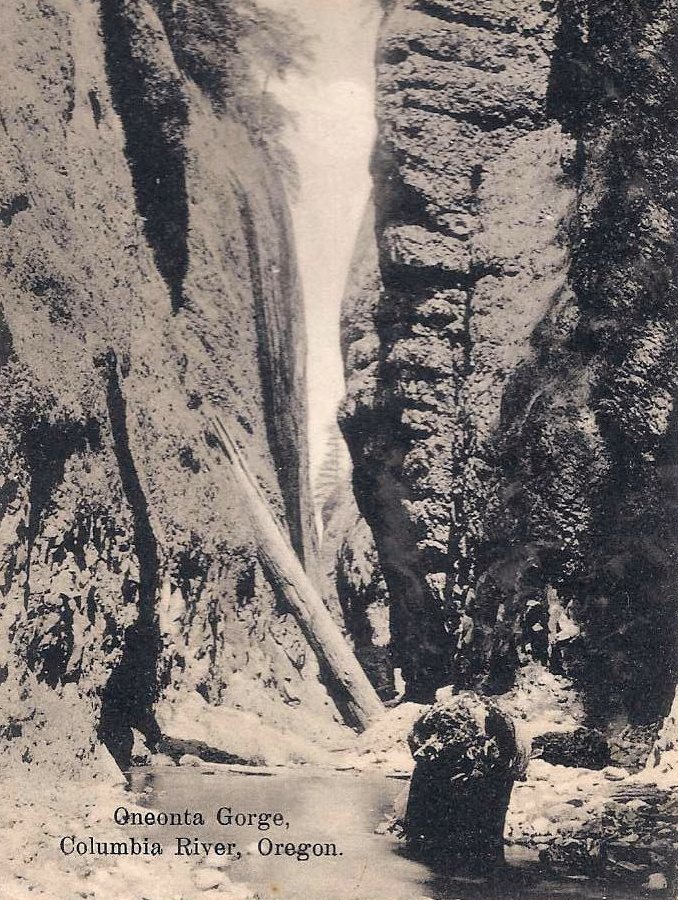
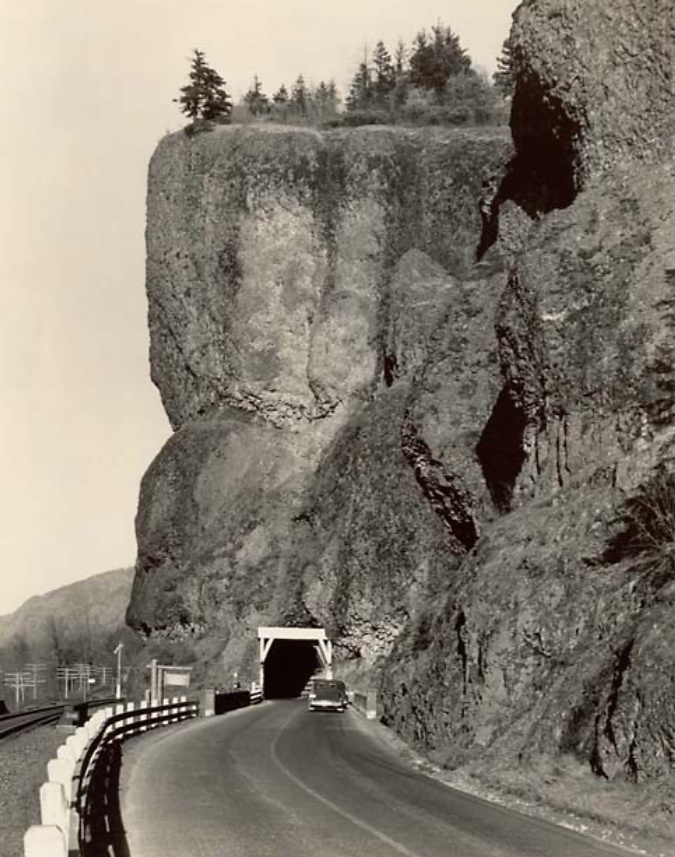
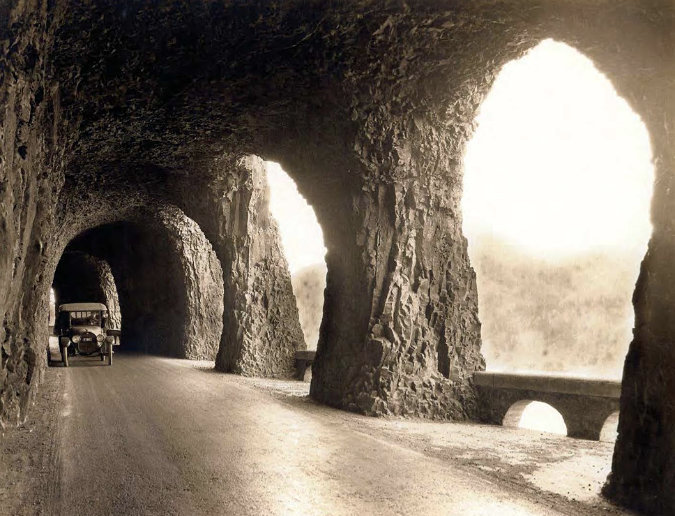
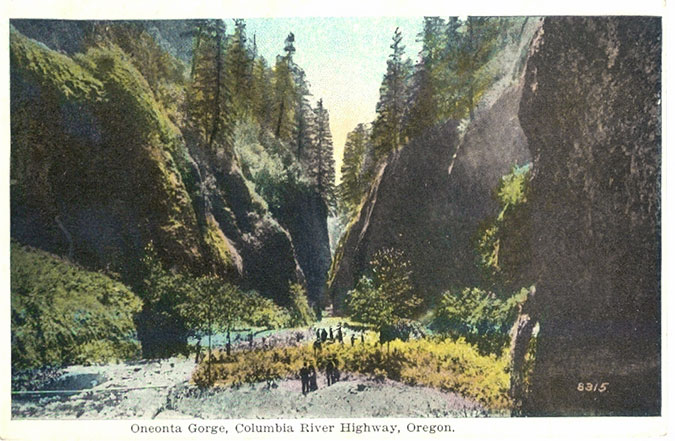
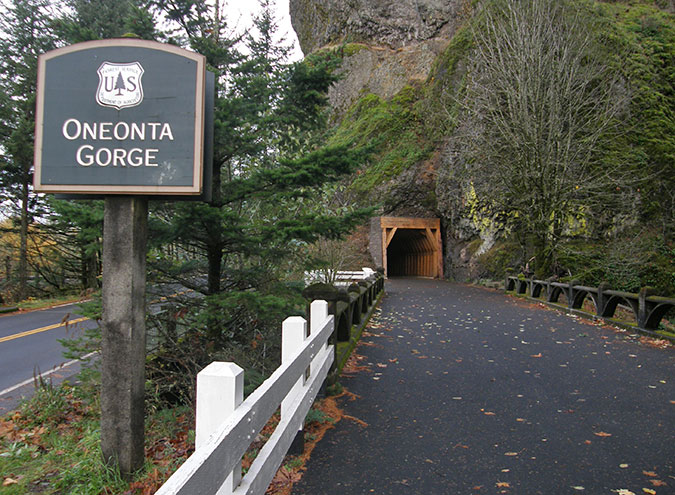
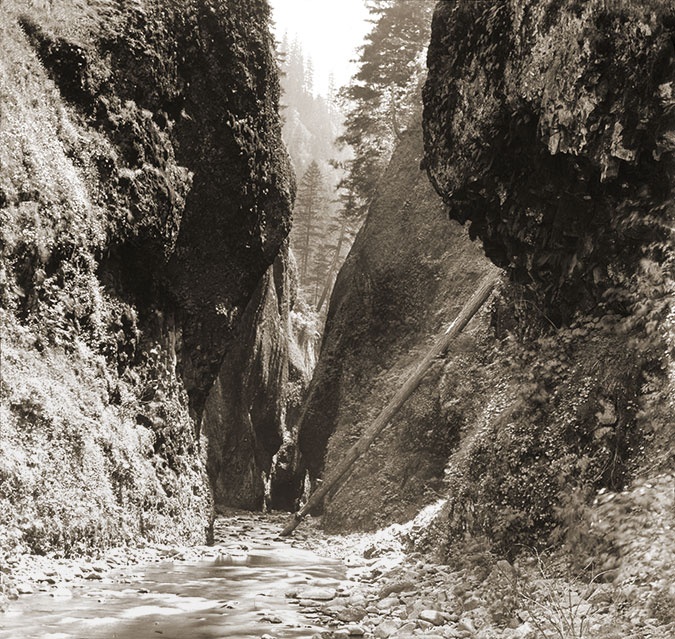
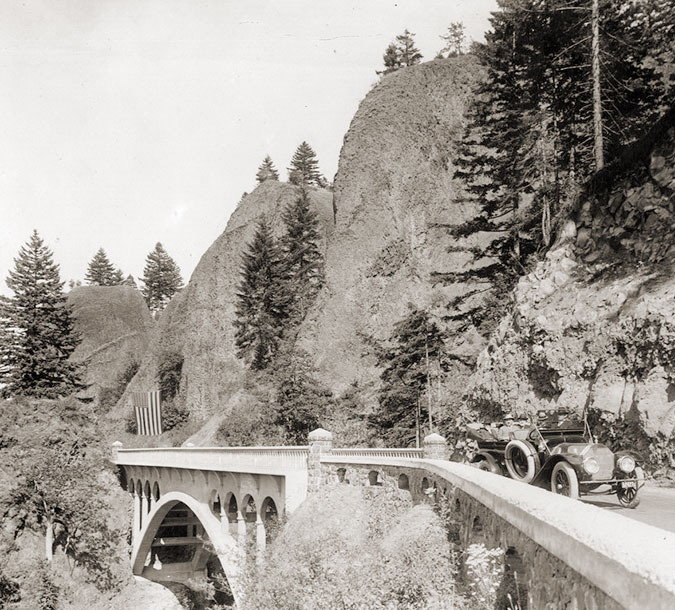
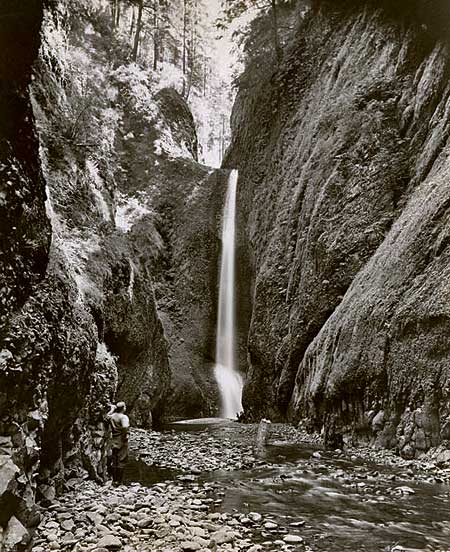
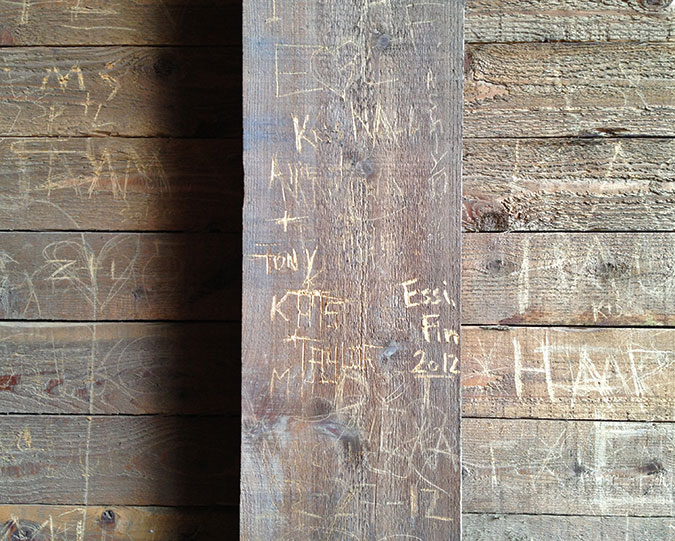Oneonta Gorge in the 1890s
Oneonta Gorge has been around since the ice age Missoula Floods shaped much of the modern landscape in the Columbia River Gorge 14,000 years ago. Yet, in the past 125 years this exquisite work of nature has endured new threats brought on by the explosion of an especially pernicious invasive species: us!
The past two decades have been especially unkind to Oneonta Gorge, with a massive wave of flip-flop wearing visitors drawn here by the invention of social media, followed by a catastrophic human-caused fire in 2017. This article is a retrospective on how we arrived at this crossroad, and what the future might hold for beautiful Oneonta Gorge.
1900-1940s: Early days at Oneonta…
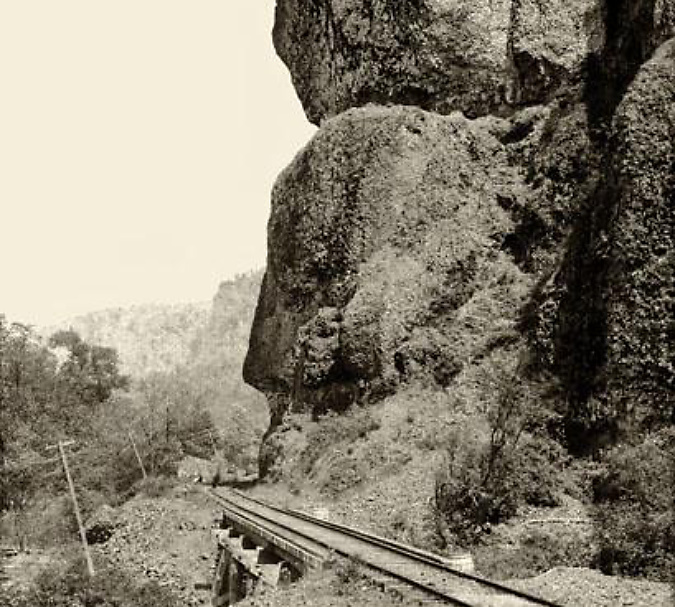
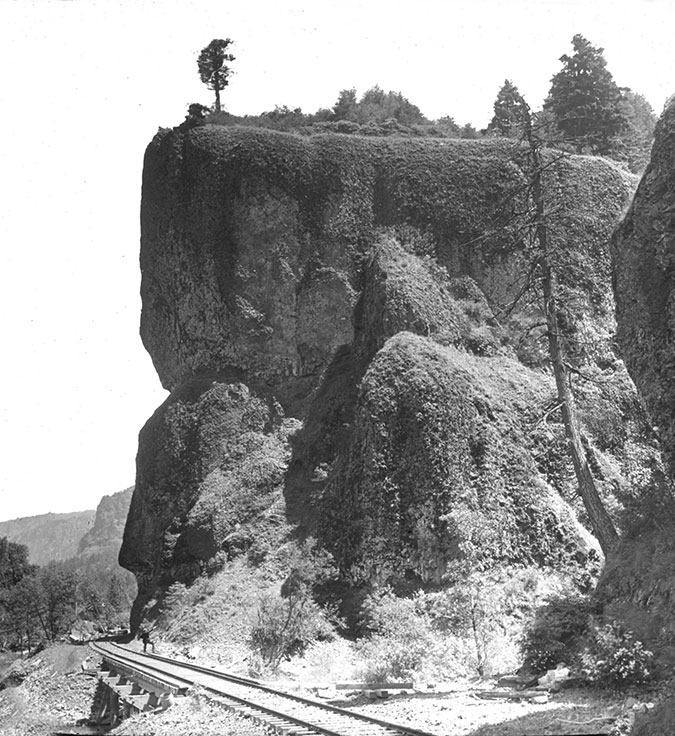
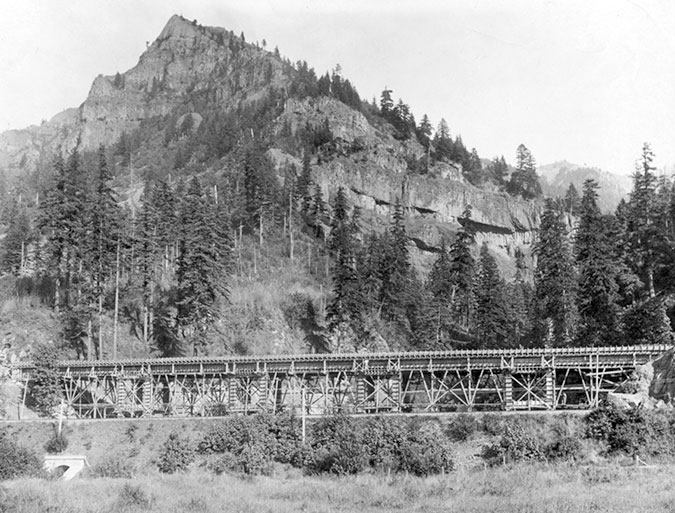
Railroad tracks had arrived at Oneonta Bluff by the 1880s
First peoples in the Pacific Northwest populated the Columbia River Gorge by the thousands for millennia, and they no doubt knew about and visited places like Oneonta Gorge, just as we do today. But it wasn’t until the transcontinental railroad was connected through the Gorge on the Oregon side in 1882 that white settlement began in earnest. Most of the early focus was on logging the big trees grew on the Gorge slopes and harvesting the seemingly endless salmon runs in the river.
That changed in the 1890s when a new stream of visitors began to follow the rails into the Gorge. Tourists, mostly from Portland, seeking the scenic wonders at each of the train stops along the way. In fact, some of the earliest parks in the Gorge were originally owned and operated by the City of Portland (including Multnomah Falls) to serve the growing interest.
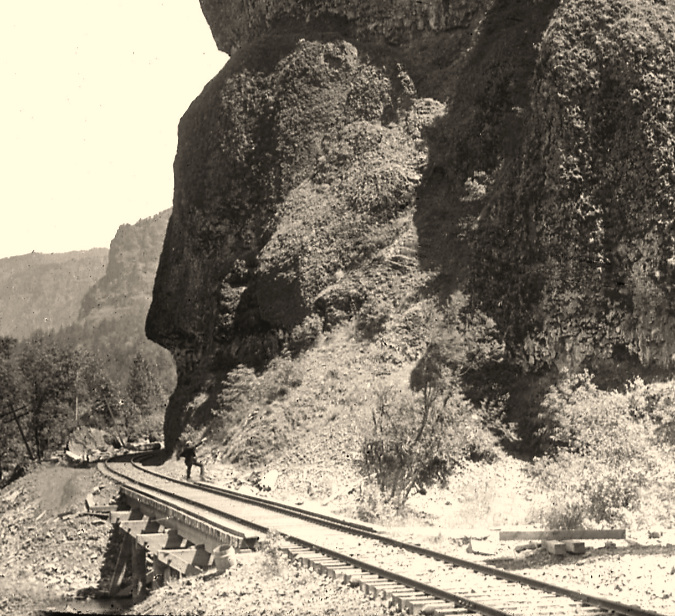
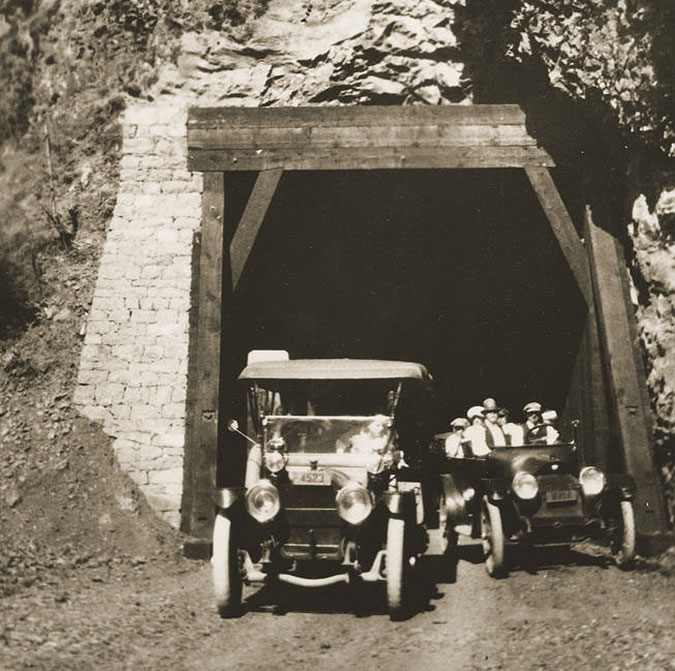
Highway surveyor – possibly Samuel Lancaster, himself –pointing to the site of the future Oneonta Tunnel in the early 1910s
The trickle turned to a tidal wave in the early 1900s, when local entrepreneur Sam Hill and his visionary road designer Samuel Lancaster opened the world-class Columbia River Highway to automobiles. Known today as the Historic Columbia River Highway, the artfully designed new road brought visitors to the Gorge by the thousands by the time it was completed in 1922, with dozens of roadside inns and restaurants springing up to serve the steady stream of motorists.
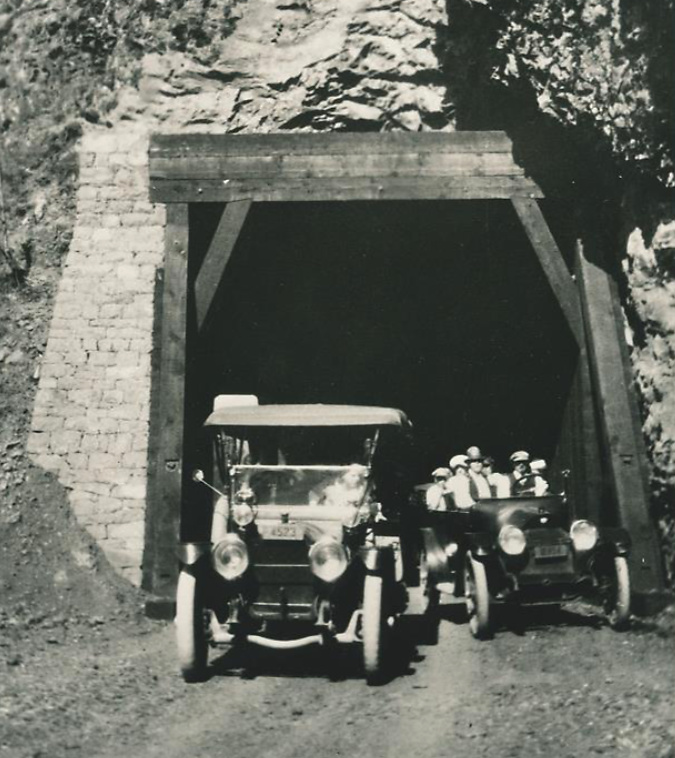
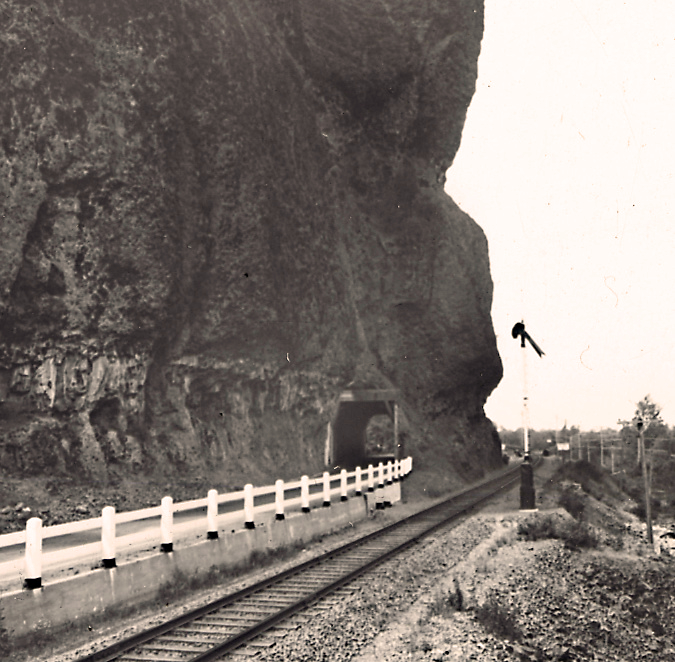
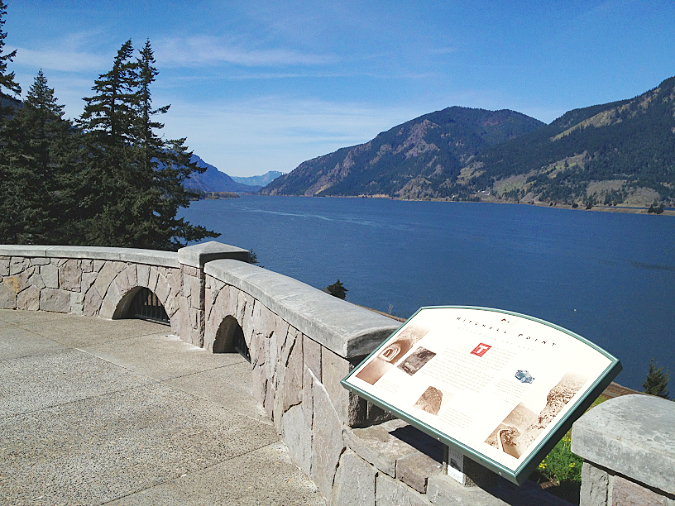
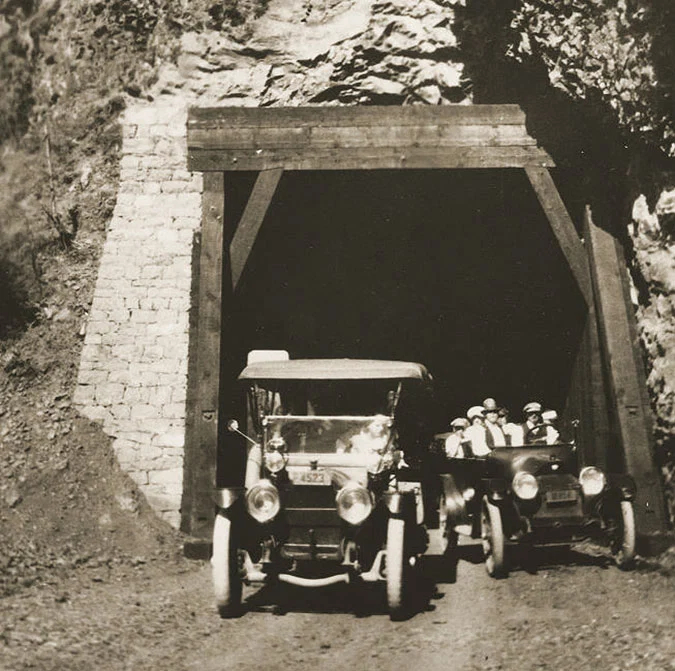
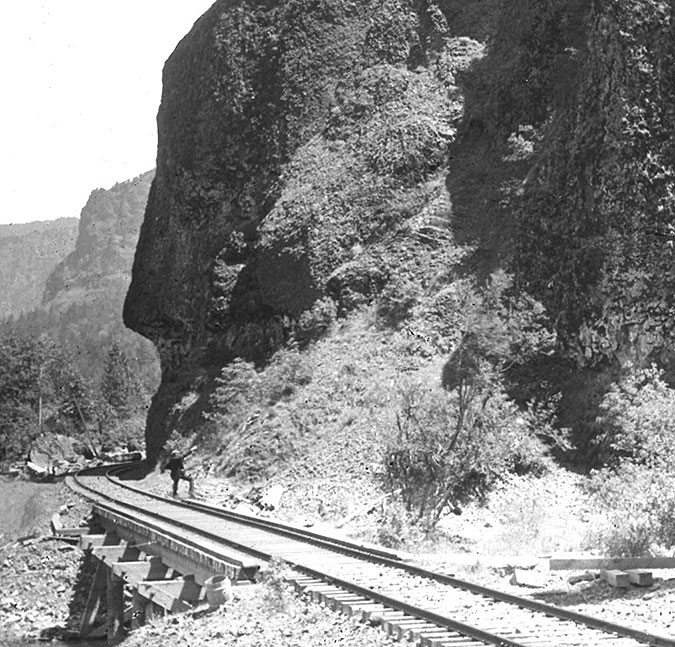
At Oneonta Gorge, Samuel Lancaster navigated a pinch point where the railroad tracks crowded the base of Oneonta Bluff by blasting a tunnel through the cliff for the new road. From the bridge at the west approach to the new tunnel, visitors also had a stunning view directly into Oneonta Gorge from their automobiles. As with other scenic spots along the road, Lancaster designed a pullout and even engineered a short, winding staircase down to the cool waters of Oneonta Creek that he knew tourists would want to explore.
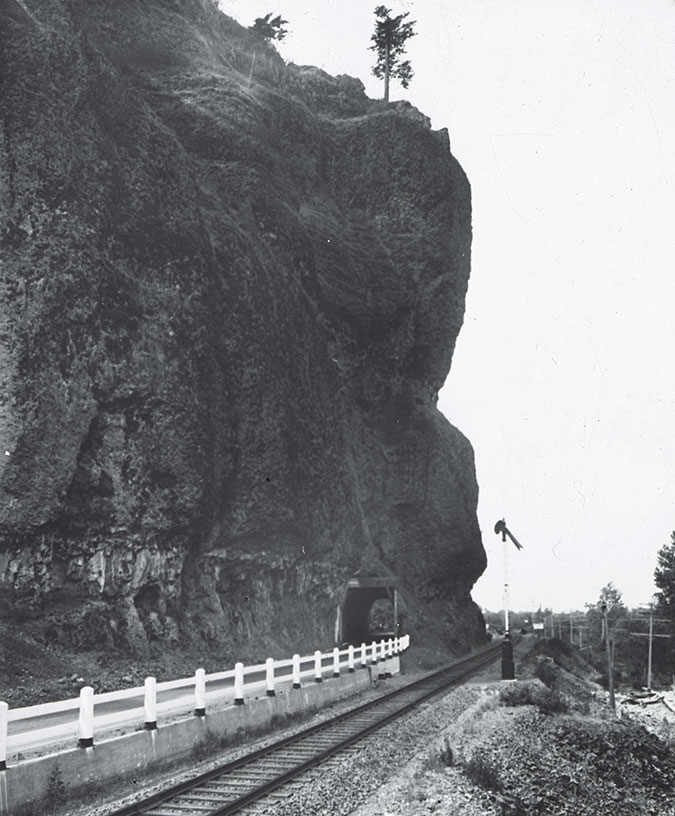
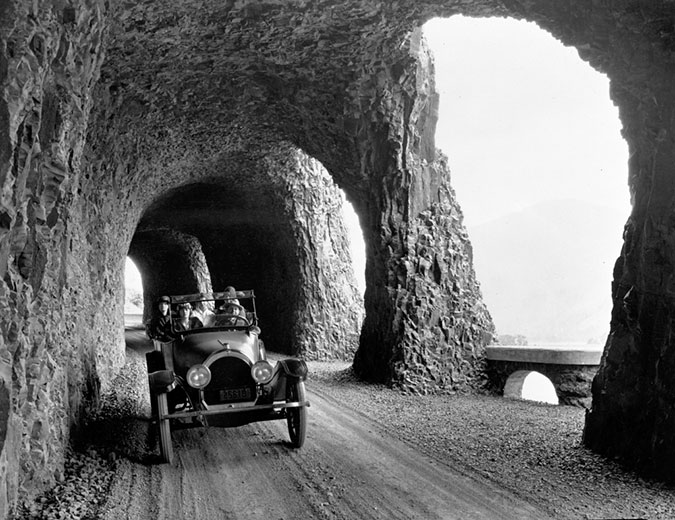
Motorists emerging from the Oneonta Tunnel in the late 1910s
The east portal to the Oneonta Tunnel in the 1920s shows how the new highway was threaded between the vertical walls of Oneonta Bluff and the railroad – the pinch point that required construction of the tunnel
Curiosity inspired more intrepid visitors to wade into Oneonta Gorge, discovering that at the south end of the 1/3 mile long box canyon you are rewarded with a rare view of beautiful Oneonta Falls. Soon, the word was out, kicking off would be become a century of weekend adventurers making their way through the narrow gorge.
Despite its unique beauty and proximity to the new road, Oneonta Gorge was spared commercial development in the early days of motorists flocking to the new highway, when tourist stops dotted the route at many of the popular scenic spots.
In the 1920s and 30s, most of the forest trails we know today were constructed by the Forest Service and Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC) to bring hikers to the series of waterfalls in the upper canyon of Oneonta Creek. These trails offered new views into Oneonta Gorge from above, though wading the creek remained the only way to reach Oneonta Falls.
Visitors at Oneonta Gorge in the early 1900s
As the popularity of the area grew, the first photos from within Oneonta Gorge and of Oneonta Falls begin to appear in postcards, travel guides and tourist folios from this era. The pair that follow from the 1930s track a hiker (perhaps the photographer?) exploring Oneonta Gorge in late summer, when the water levels are typically low. Well into the 1990s, the trip through Oneonta Gorge was much like this, with just a few knee-deep pools to navigate in reaching the falls.
Oneonta Gorge and hiker in the 1930s
Oneonta Falls and hiker in the 1930s
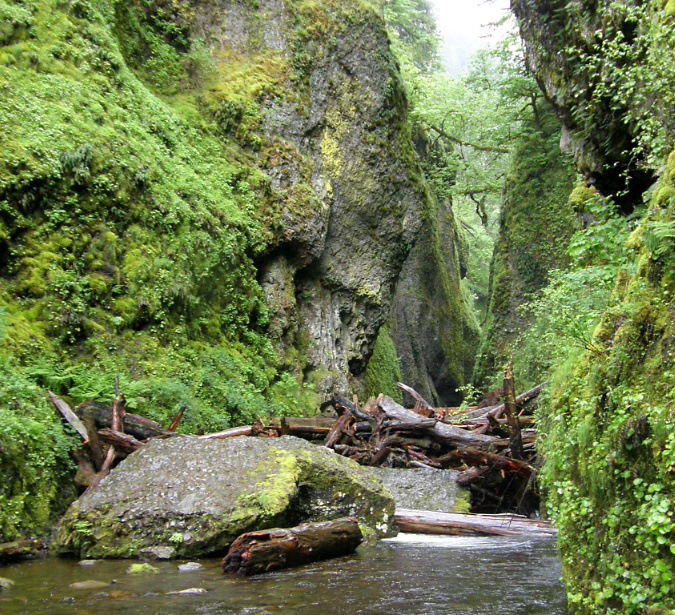
This postcard view (below) from the 1930s is notable in showing boulders and a large log blocking Oneonta Gorge. From my own experiences there, the route was clear of debris on this scale from the mid-1970s until the rockfall that triggered the modern logjam in the late 1990s. What happened to the debris in this photo? They were simply broken up and swept away.
1930s postcard showing boulders and logs in Oneonta Gorge similar to today
Oneonta Gorge was created by a perpetual cycle of erosion, with the stream continually undercutting the vertical basalt walls, then clearing boulders and debris that periodically collapses into the stream. During high runoff events from November through March, Oneonta Creek can become a raging torrent, with enormous hydraulic force that can easily move whole trees and large boulders downstream, eventually breaking them apart into smaller, even more easily transported rock and debris the process (more on that toward the end of this article).
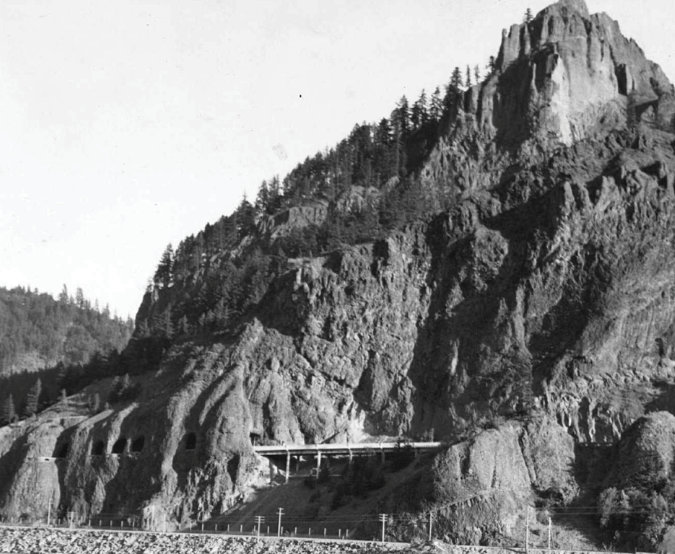
The tunnel at Oneonta Creek was an uncomfortably tight squeeze for passing vehicles from the beginning, so when the railroads moved their tracks away from cliffs of Oneonta Bluff sometime in the early 1940s, ODOT took the opportunity to move the road and bypass the old tunnel.
Oneonta Tunnel in the early 1940s with the relocated railroad line already away from the bluff
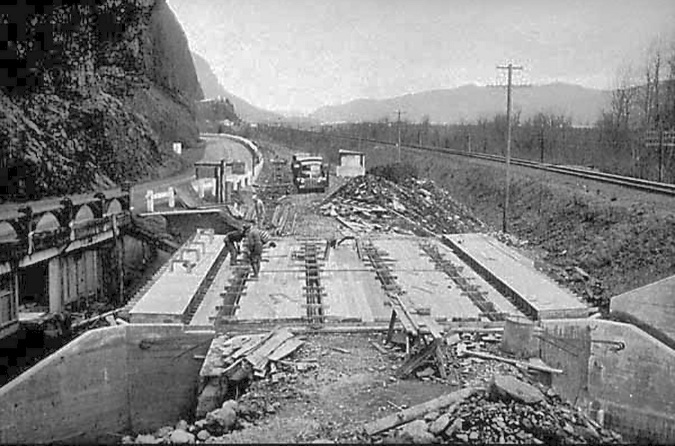
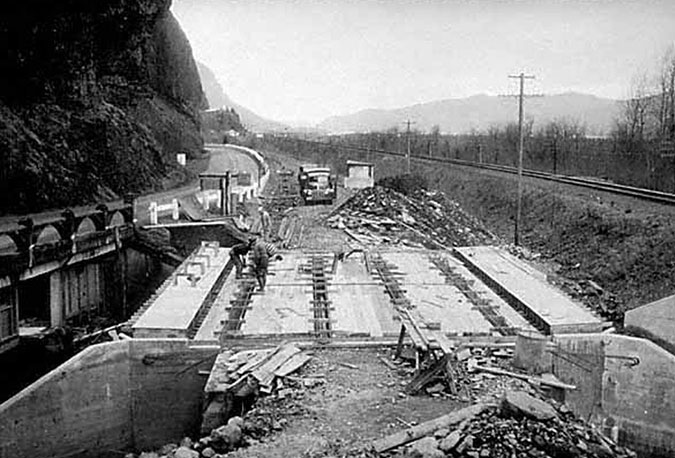
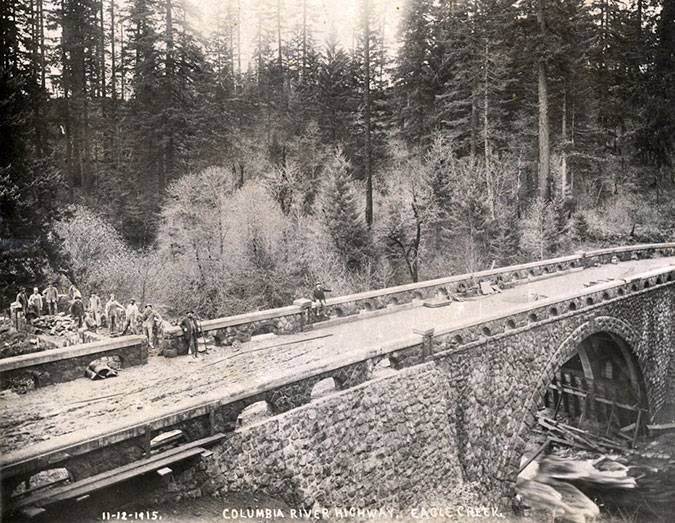
The tunnel bypass involved constructing a new bridge over Oneonta Creek (below), immediately adjacent to the old bridge. Both bridges survive today, with the newer bridge serving as the Historic Columbia River Highway route and the original bridge leading pedestrians and cyclists to the restored Oneonta Tunnel.
“New” highway bridge bypassing the Oneonta Tunnel under construction in 1948. The original bridge can be seen on the left
The tunnel bypass was completed in 1948 (below), and both ends of the Oneonta Tunnel were blocked with fill to prevent access. The original highway stub over the old bridge was left in place as a wayside for visitors to Oneonta Gorge.
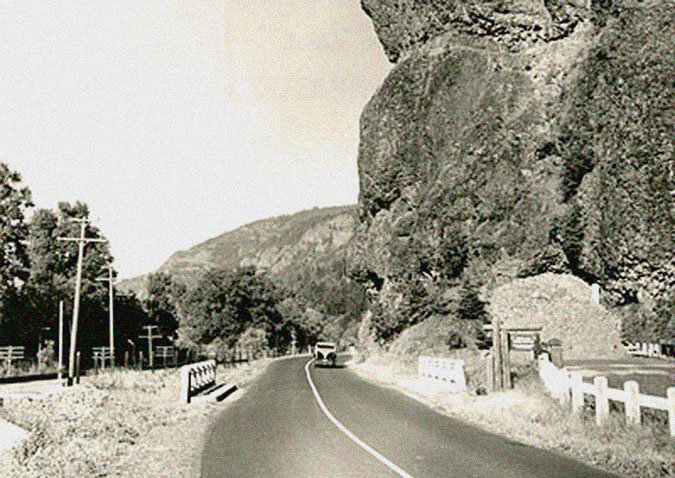
The completed bypass in the early 1950s with the old tunnel blocked with fill
The Oneonta Tunnel bypass in 1948 was part of a larger effort by the Oregon Highway Division to realign the original Columbia River Highway as a river-level route, completely bypassing whole sections, including the famous loops that climb over Crown Point and Rowena Crest.
Much of this work was completed by the early 1950s, but in 1956 the federal Interstate and Defense Highways Act set construction of today’s Interstate-84 in motion, relegating the original versions of the Columbia River Highway to scenic routes in some areas, and being completely abandoned in others.
That might have been the end of the story for the mothballed Oneonta Tunnel, save for the following provision in the 1986 Columbia River Gorge National Scenic Area legislation:
This unique provision was way ahead of its time in our country by recognizing the historic and recreation value of old, “obsolete” roadways. Since then, ODOT has steadily worked toward this bold vision with a string of exceptional restoration projects. As we approach the 40th anniversary of the scenic area legislation, a completely restored and reconnected historic route from Portland to The Dalles is on track to become a reality.
2003-09: Restoring the Oneonta tunnel and bridge
ODOT renovated the original Oneonta Bridge in the 2003
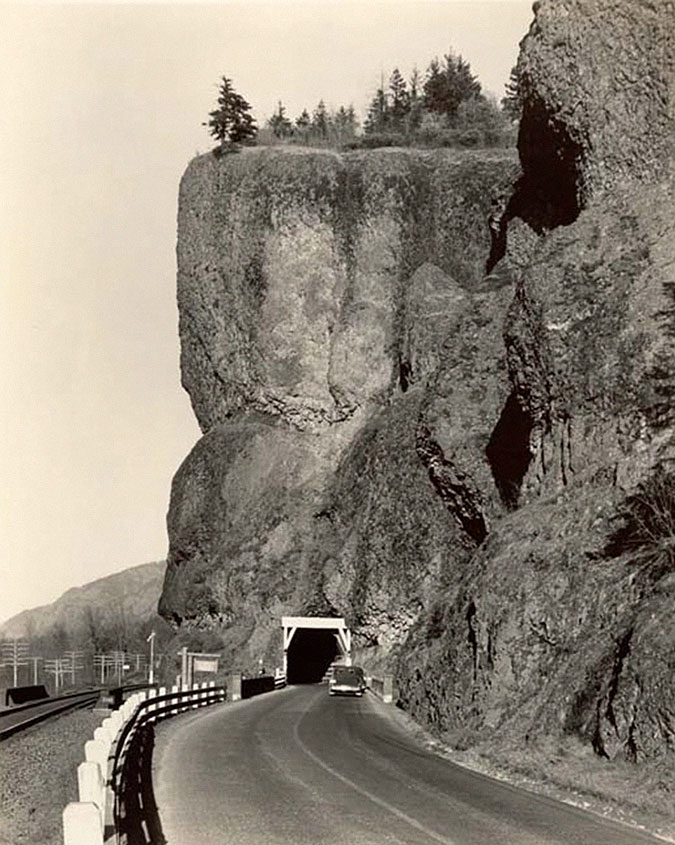
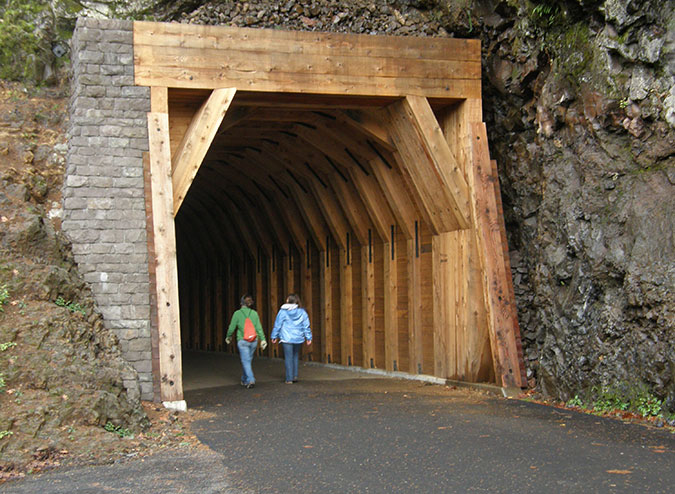
At Oneonta, the historic highway restoration included renovating the original highway bridge (above) and reopening the Samuel Lancaster’s original tunnel (below) after fifty years of closure. The 1948 tunnel bypass allowed for this segment to be reimagined as a pedestrian route, bringing visitors through the restored tunnel to a dramatic view from the historic bridge into Oneonta Gorge.
The newly excavated Oneonta Tunnel in 2006
Restoration of the east portal to the Oneonta Tunnel in 2006
Restoration of the west portal to the Oneonta Tunnel in 2006
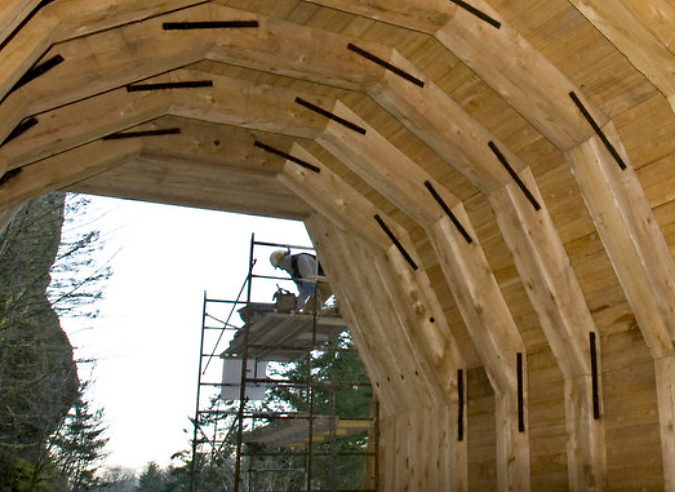
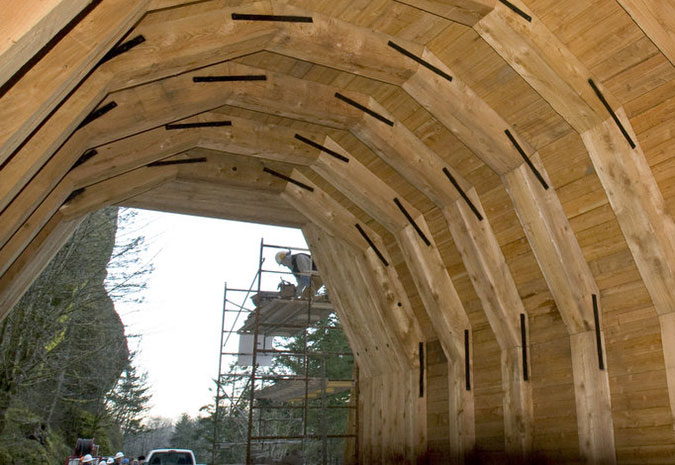
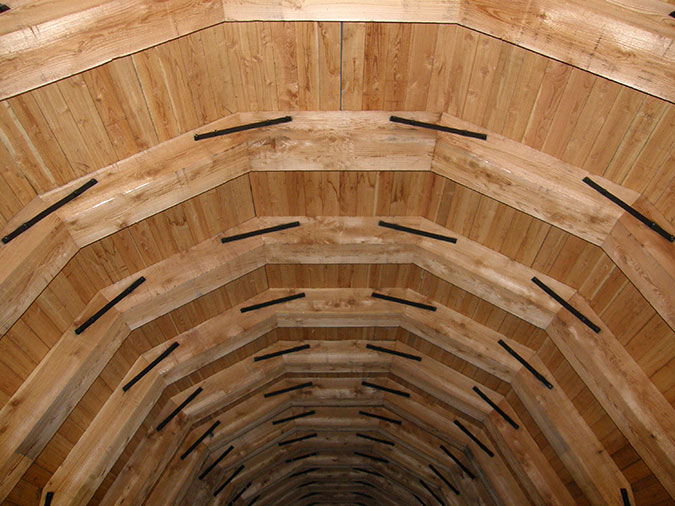
The tunnel restoration included recreating the stonework surrounding both portals and a completely rebuilt, wood tunnel lining (below).
Construction of the wood interior lining in the restored Oneonta Tunnel
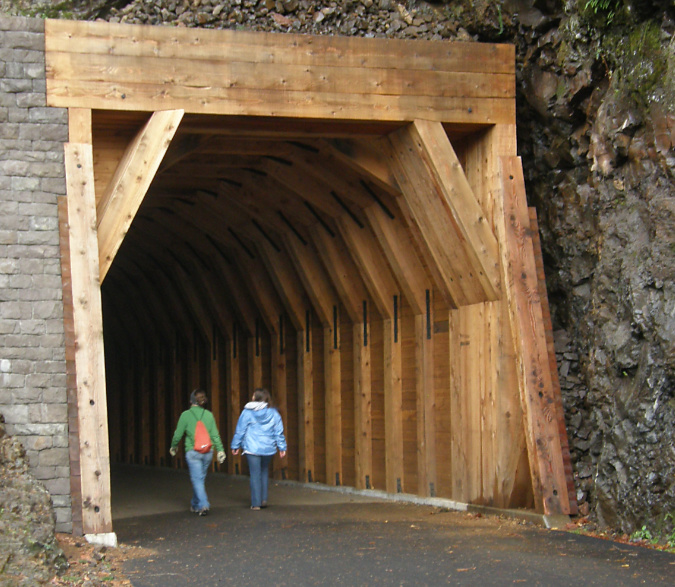
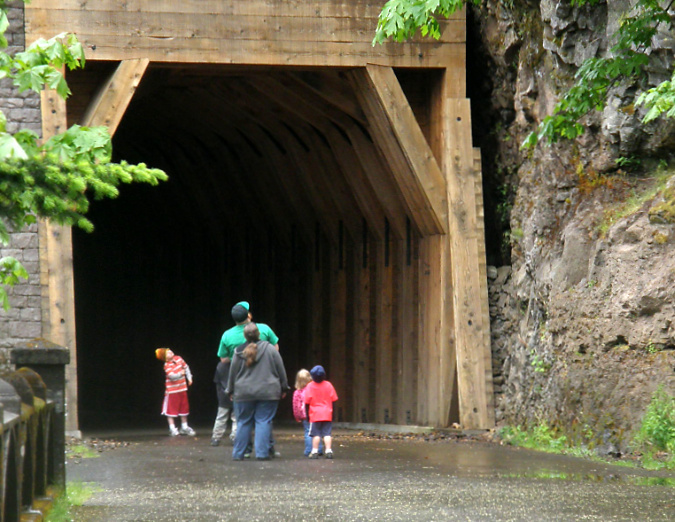
The newly restored tunnel was opened to the public in 2009. For hikers, the new route connected a hiking loop between the Oneonta and Horsetail trail systems. For motorists, it was a new place to explore among the traditional stops along the historic highway.
Hikers using the newly restored Oneonta Tunnel in 2009
Family exploring the newly restored Oneonta Tunnel in 2009
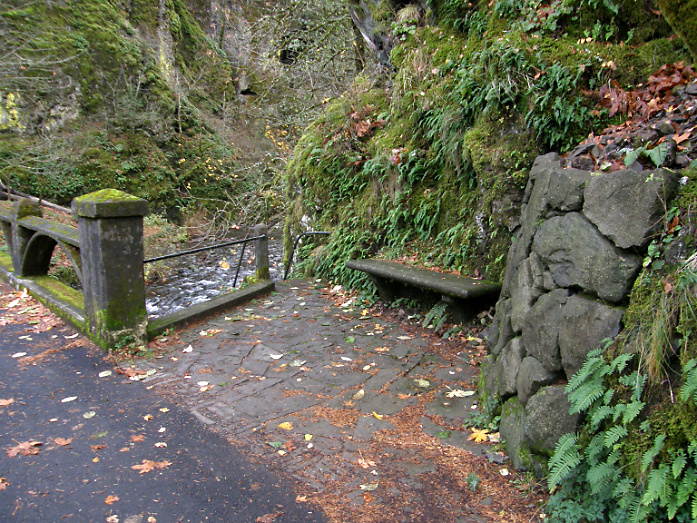
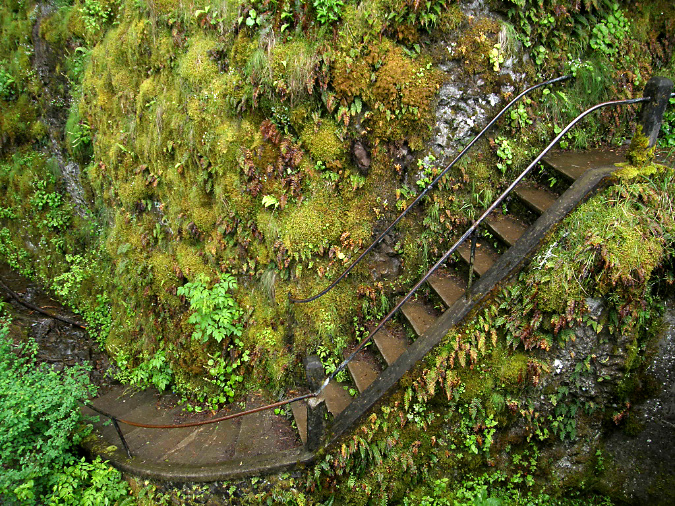
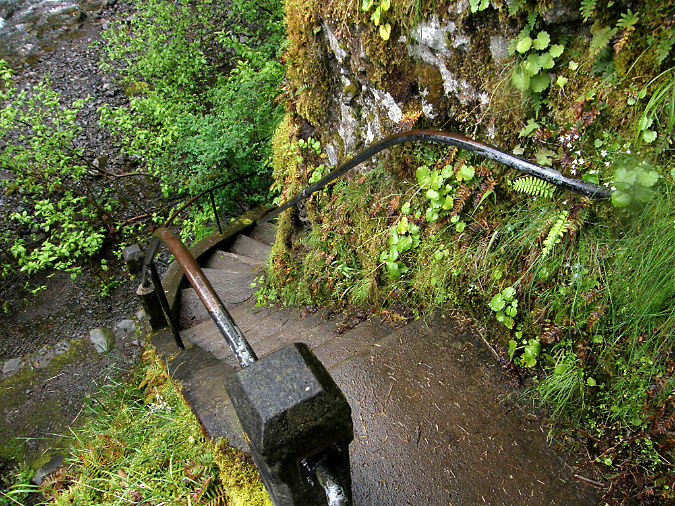
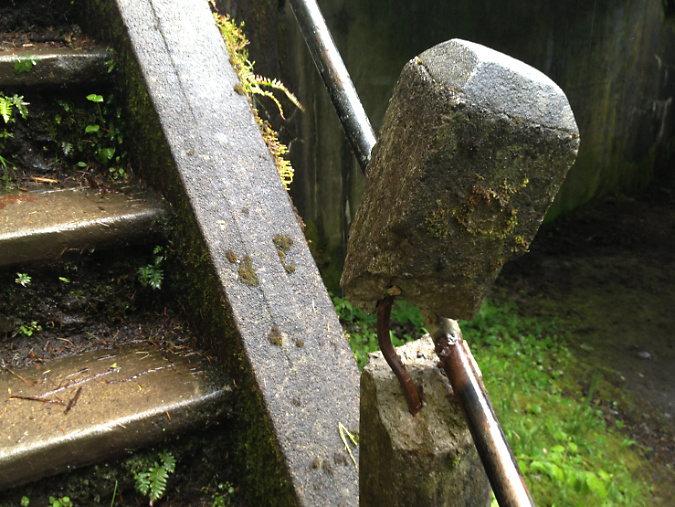
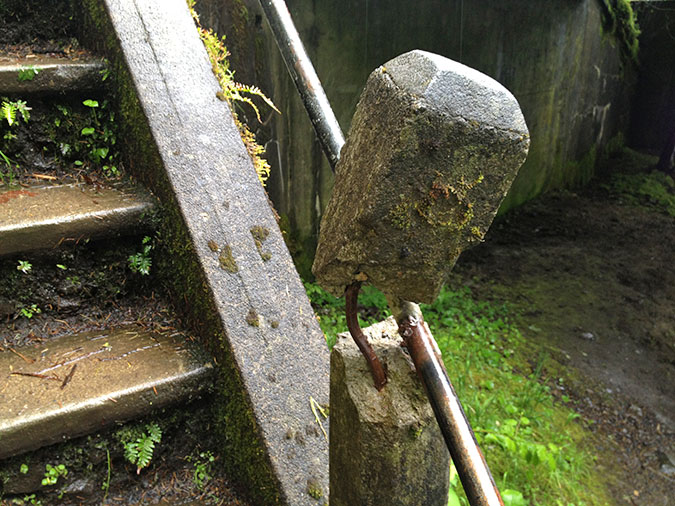
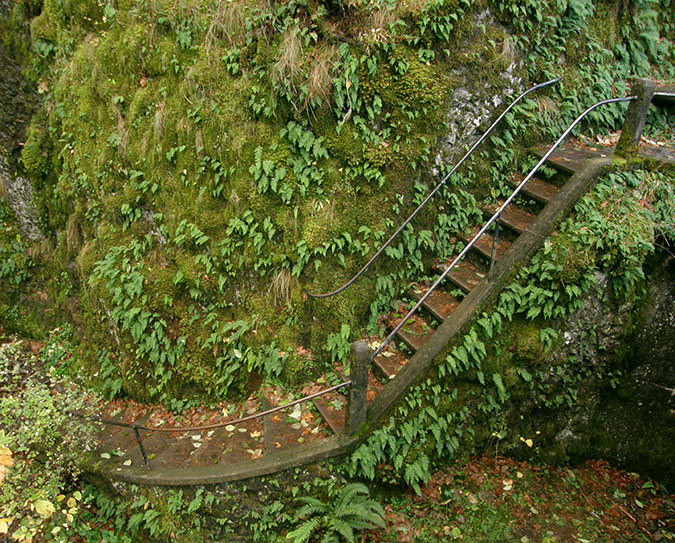
The Oneonta Bridge restoration included work at the west abutment, where a small alcove with an ornate bench from the original design was refurbished. This unassuming spot is one of the most delightful features in Samuel Landcaster’s vision for the highway. Knowing that visitors would want to explore, he built a tiny, winding staircase that hugs the cliff as it descends from the alcove to Oneonta Creek (below). The stairway is a fun surprise for visitors who stop, as it is not visible from the road.
Restored alcove and bench at the head of the winding staircase to Oneonta Creek in 2009
Historic winding staircase at Oneonta Creek in 2009
Looking down the historic winding staircase at Oneonta Creek in 2009
When these carefully crafted restoration efforts at Oneonta were finally opened to the public in 2009, few could imagine the impact that social media was about to unleash in the Gorge. Facebook had been founded in 2004, but only began its explosive growth in 2007, doubling from 50 million users to 100 million in 2008. It would reach a staggering 1 billion users by 2012. Instagram soon added to the impact after it was founded in 2010, reaching 10 million users within a year and 1 billion users by 2018.
2010: The logjam + social media era…
The Oneonta logjam in 2011
When you consider the recreation infrastructure in the Gorge – the trails, campground, picnic sites, scenic highway, Vista House and the lodge at Multnomah Falls – are much the same as they were in the 1930s, it’s surprising that the exponential growth in visitors in recent decades hasn’t been more destructive. That said, the arrival of social media, and its ability to concentrate large crowds overnight, impacted the Gorge, and especially Oneonta, like no nothing before.
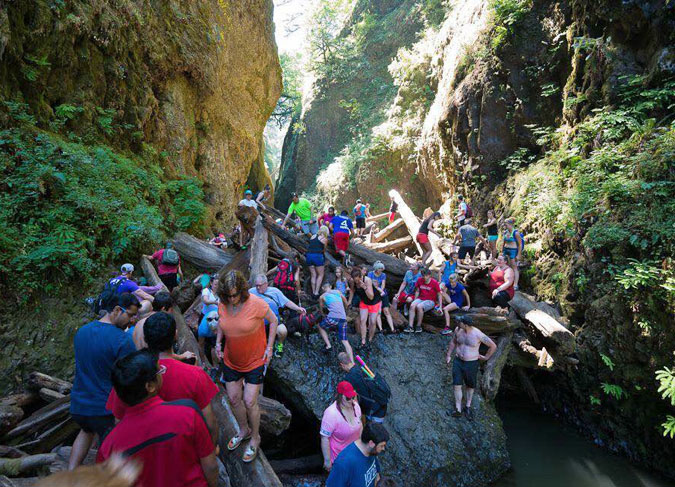
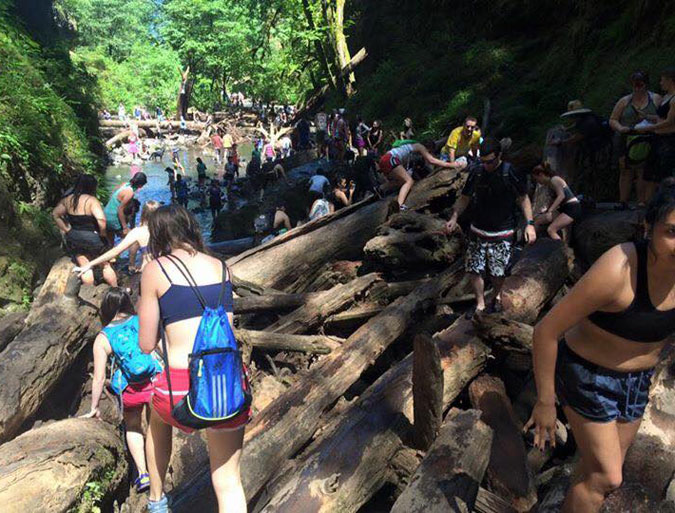
Compounding the “Instagram-effect” of social media in the years that followed reopening of the tunnel, the pair of van-sized boulders that had collapsed into the lower entrance to Oneonta Gorge in the late 1990s had stacked up enough logs to become a true hazard to cross. In the beginning, the boulders themselves weren’t difficult to navigate, but as log pile continued to grow, crossing the obstacle became a risky venture for social media novices drawn here by nothing more than a viral Instagram selfie.
The Forest Service had posted a hazard warning around 2010, but Oneonta Gorge remained opened to the crowds that were growing exponentially each summer, and the signs went completely unnoticed by the growing horde.
Logjam warning sign in 2011
The growing summer crowds at Oneonta Gorge were beginning to impact the newly restored Oneonta Tunnel, as well. For anyone who loves the Gorge, it was maddening to see vandalism to the pristine wood lining in the tunnel when it started to appear in 2012. The heavy crowds eventually impacted other features, including damage to the railing on the historic, winding staircase (below) and the fragile ecosystem of Oneonta Gorge, itself. It was a classic tragedy of the commons in the making, with the Forest Service seemingly paralyzed from intervening.
Vandalism began to appear in the Oneonta Tunnel by 2013
Damaged staircase railing at Oneonta in 2013
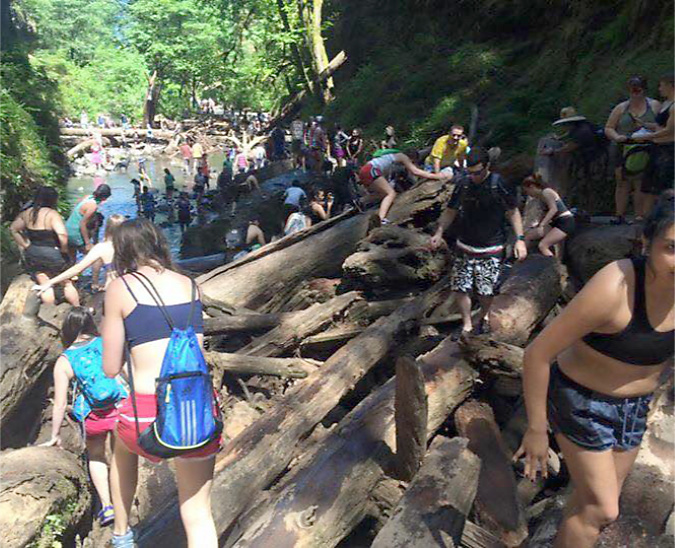
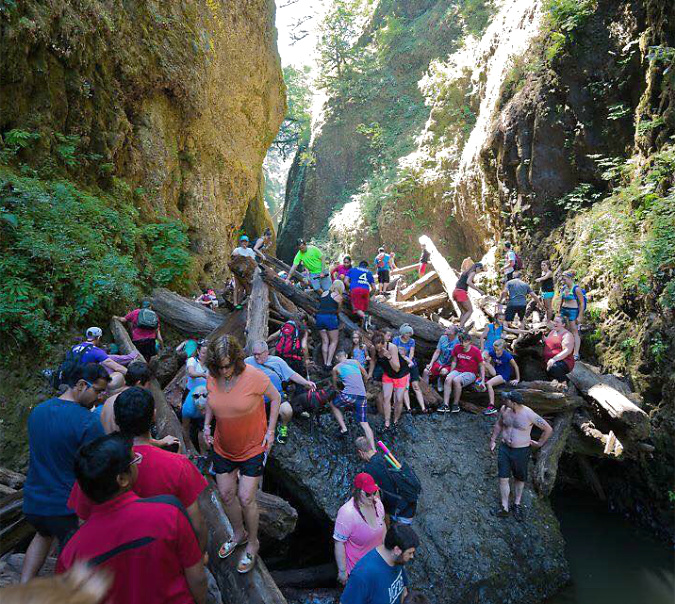
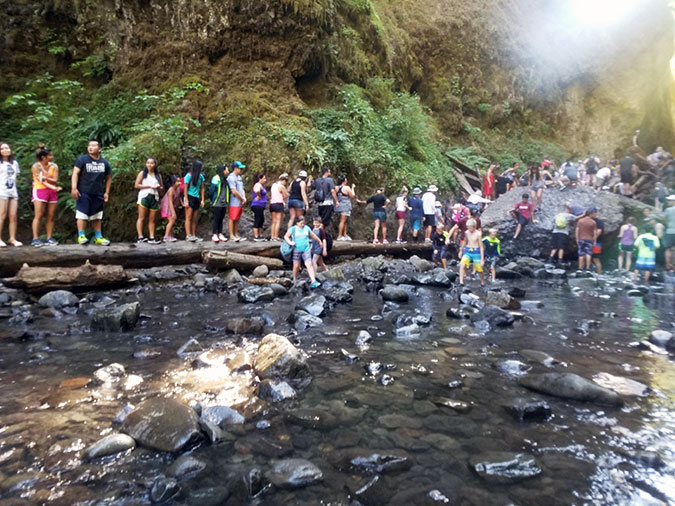
By 2015, the full brunt of social media – now including still more youth-oriented online platforms, like SnapChat and Reddit – was all too apparent at Oneonta Gorge. Summertime traffic came to a standstill on the old highway, with parked cars lining the shoulders in both directions and overflowing into the nearby Horsetail wayside.
Oregon photographer extraordinaire T.J. Thorne (and a friend of the blog!) captured the following images that summer that describe the mayhem in ways words cannot match.
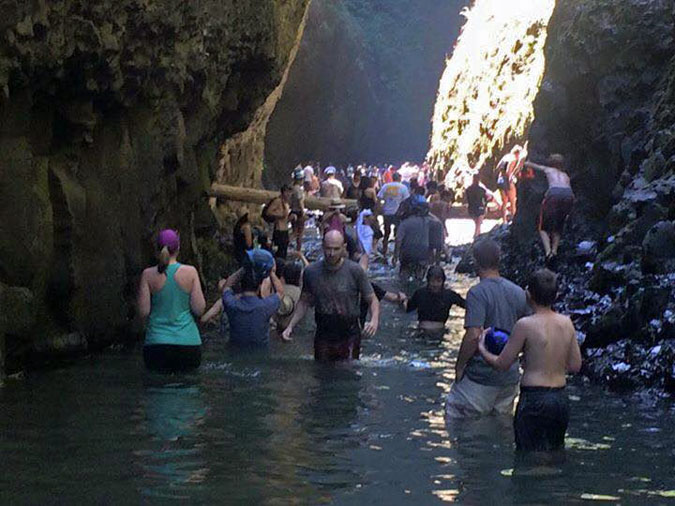
Social media crowds overwhelming Oneonta Gorge in the summer of 2015 (T.J. Thorne)
Crowds at Oneonta Gorge in the summer of 2015 (T.J. Thorne)
Vandalism in the tunnel spiked with the mobs, too, and by 2015 the beautifully restored walls had been almost completely destroyed by the thoughtless members of the summer crowds. Still more discouraging is that the damage was largely wrought by Millennials – a generation supposedly more in touch with environmental awareness, sustainability and mutual respect than any before it.
Vandalism overwhelmed the Oneonta Tunnel by 2015
Heavy vandalism to Oneonta Tunnel in 2015
Tragically, at least one person was killed while crossing the log jam during this unhinged period, and there’s no way to know how many were injured – nor what the environmental price to the unique ecosystem in Oneonta Gorge has been from so many people pouring into this relatively tiny space. Yet, there was still no effort by the Forest Service to limit or manage access… that is, until the Eagle Creek Fire in 2017.
2017: Gorge Fire… and the future?
The Eagle Creek Fire as viewed from the Washington side of the Gorge in September 2017
The Eagle Creek Fire in 2017 reset everything in the Gorge. It was the first major fire since around 1900, yet was also somewhat typical of fires that have always burned in the Gorge. The only thing new about the event was the level of human development and activity that has come to the Gorge since the last big fire, underscored by the fact that it was a human-caused fire set off by a young hiker lighting fireworks on the Eagle Creek Trail.
The Oneonta Creek watershed was hit especially hard by the fire, with much of the upper basin completely burned. The immediate aftermath of the burn was a lot of surface erosion and falling trees killed by the fire. More locally, the fire killed trees and loosened rocks and debris along the rim of Oneonta Gorge, creating an immediate hazard to anyone below.
Aerial view of the fire impact along Oneonta Gorge in late 201. Oneonta Falls can be seen at the far end of the gorge in this view
Aerial view of fire impact to Oneonta Gorge and the larger watershed in the distance in 2017
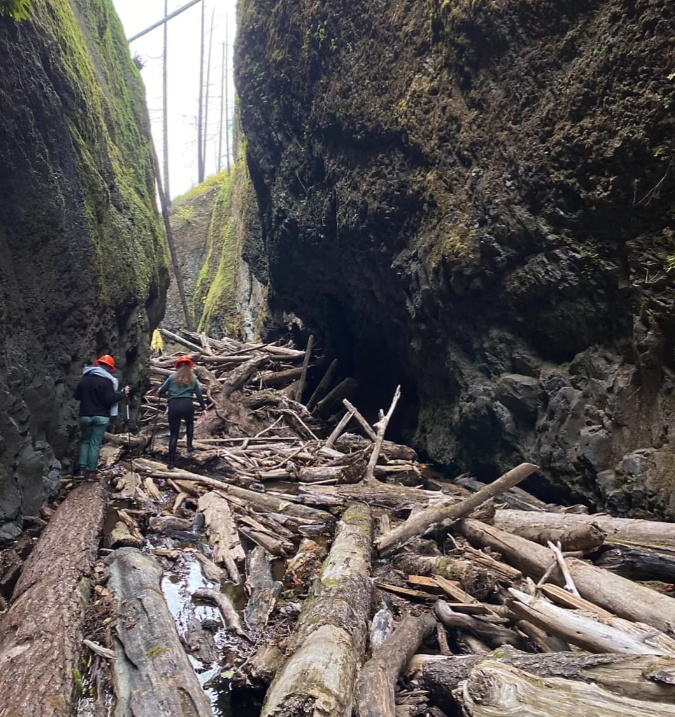
Over time, the extensive burn upstream has released hundreds of logs into Oneonta Creek, with many more to come. It didn’t take long for winter storms to carry these logs and other debris downstream to Oneonta Gorge, where the logjams have now grown to epic proportions.
Forest Service crew documenting the growing, post-fire logjams in Oneonta Gorge in 2023 (USFS)
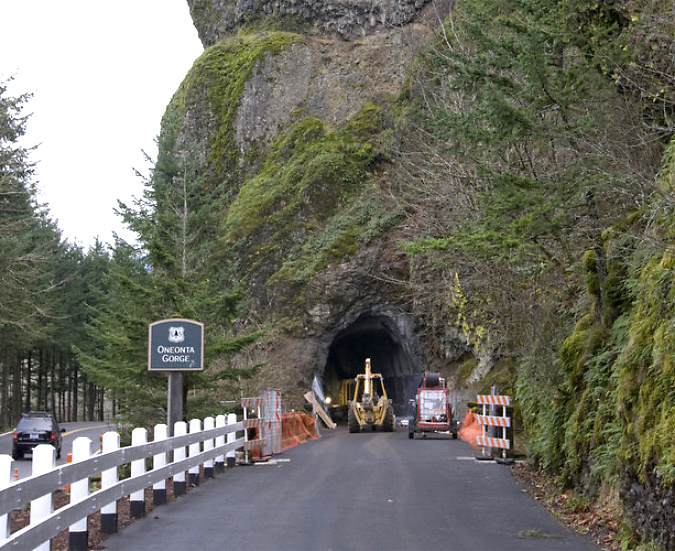
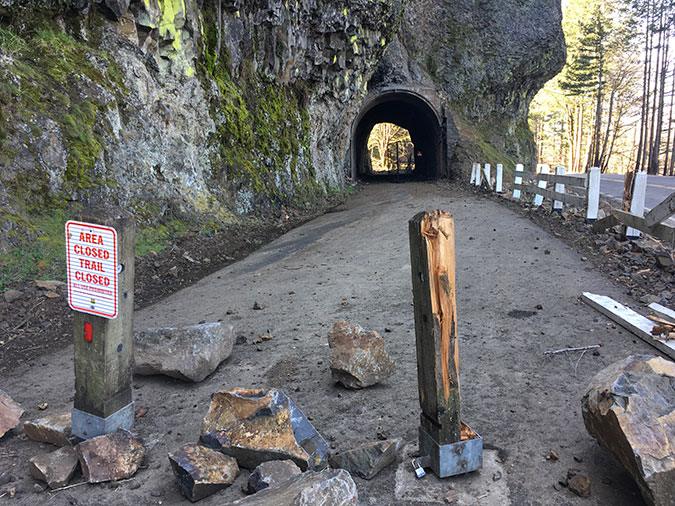
Most of the burn was immediately closed to the public after the fire, but the Forest Service has gradually reopened much of the area as trails are cleared and the forest recovery takes hold. An exception is Oneonta Gorge, however, where the agency continues to prohibit public access.
That’s a good thing, and overdue. Nobody knows how long it will take for Oneonta Creek to clear the logjams from Oneonta Gorge, but the hazards they create should at least help the Forest Service take the time to enact a new access policy that limits when and how many people are allowed to enter the gorge.
Oneonta Gorge sign announcing indefinite closure following the 2017 fire
Statesmen Journal outdoor reporter (and another friend of the blog!) Zach Urness recently reported on Forest Service plans to consider reopening Oneonta Gorge later in this decade. According to Zach’s reporting, the agency will consider these options for the future:
1) Unrestricted access
2) Complete closure to access
3) Seasonal public access outside of salmon and steelhead spawning
4) Open or seasonal public access with trigger points to limit use
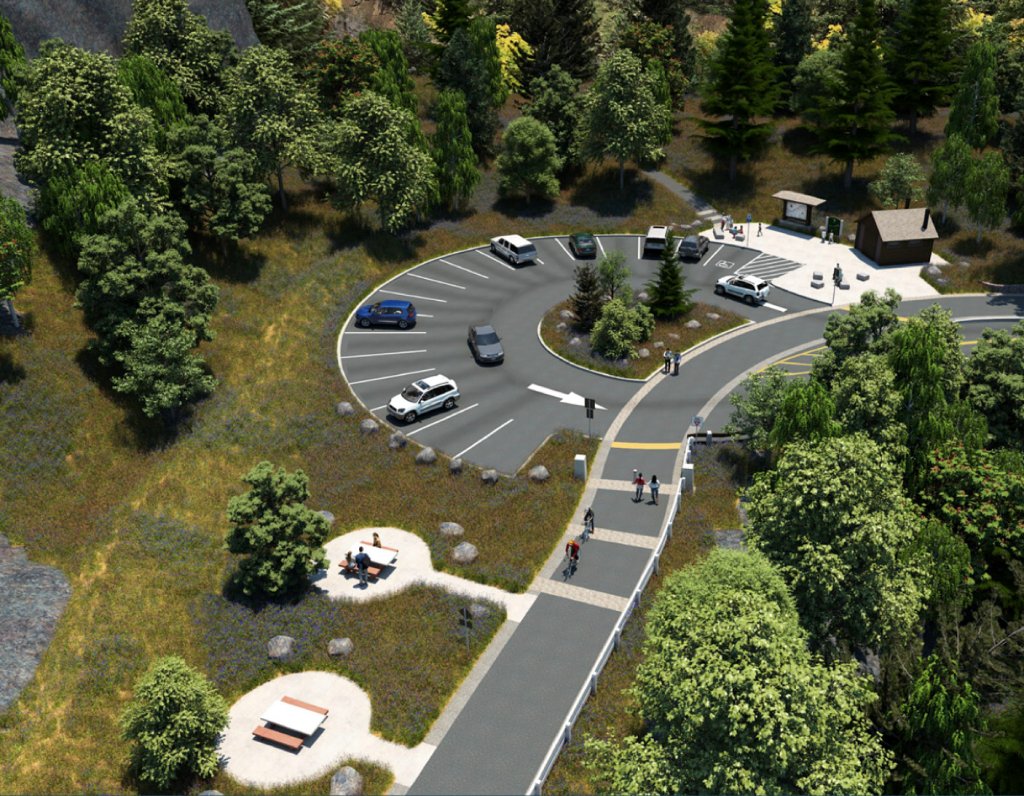
My hope is that something like the fourth option will be pursued in the interest protecting Oneonta Gorge from being loved to death in the future. The Forest Service planning effort will begin later this year.
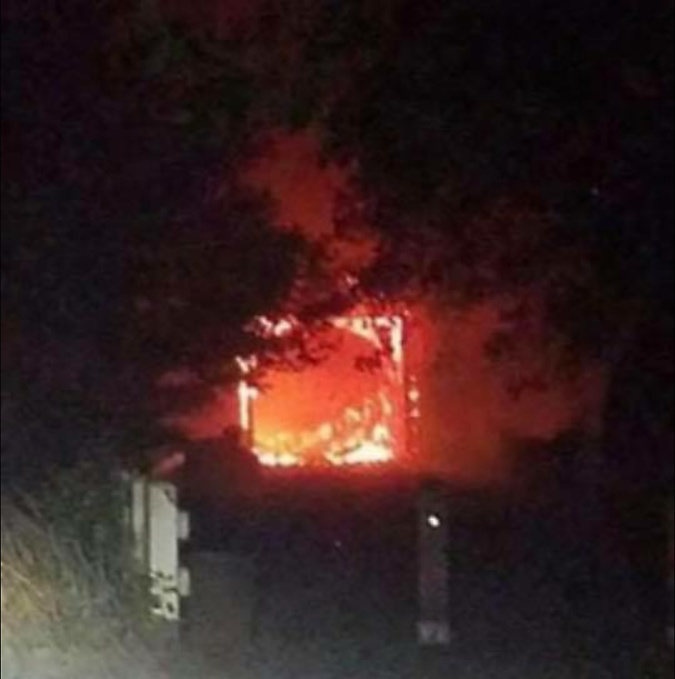
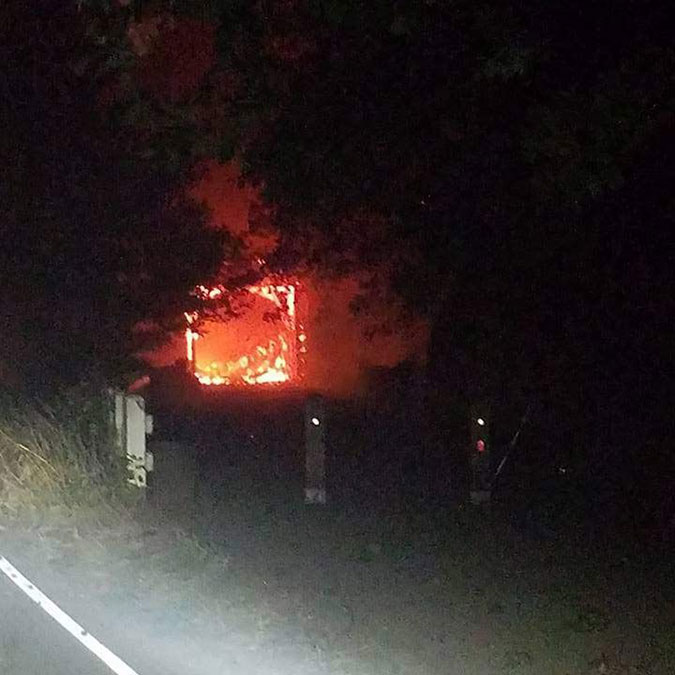
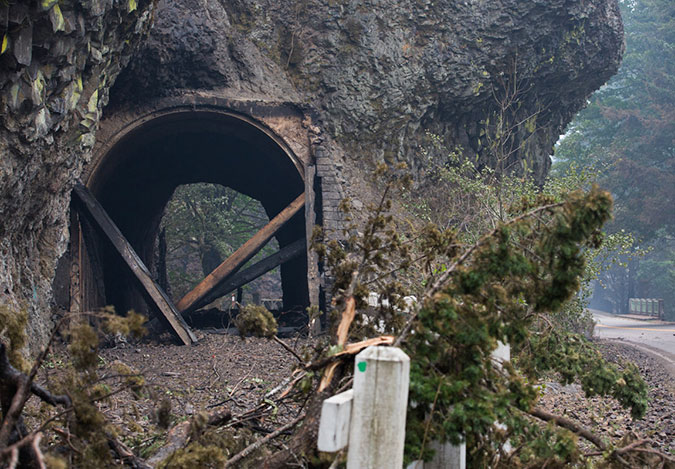
The Oneonta Tunnel became an inferno during the 2017 Eagle Creek Fire (USFS)
The fire had a devastating impact on the Oneonta Tunnel, as well. When I saw the above image of the tunnel in flames during the 2017 Eagle Creek Fire, I had mixed emotions: the first was sadness over the loss of this beautifully restored piece of our history, and the second was a sense of opportunity. If the tunnel were restored again, perhaps this time it could be more closely managed to prevent the grotesque scale of vandalism that had defaced it before the fire?
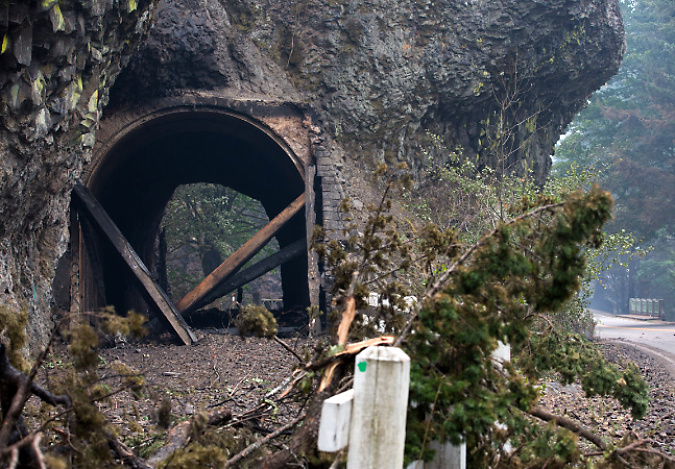
West portal to the Oneonta Tunnel immediately after the 2017 fire (ODOT)
East portal to the Oneonta Tunnel immediately after the 2017 fire (ODOT)
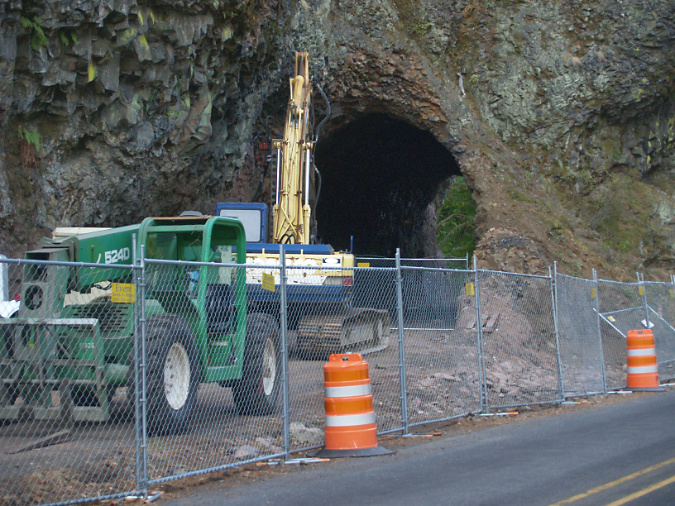
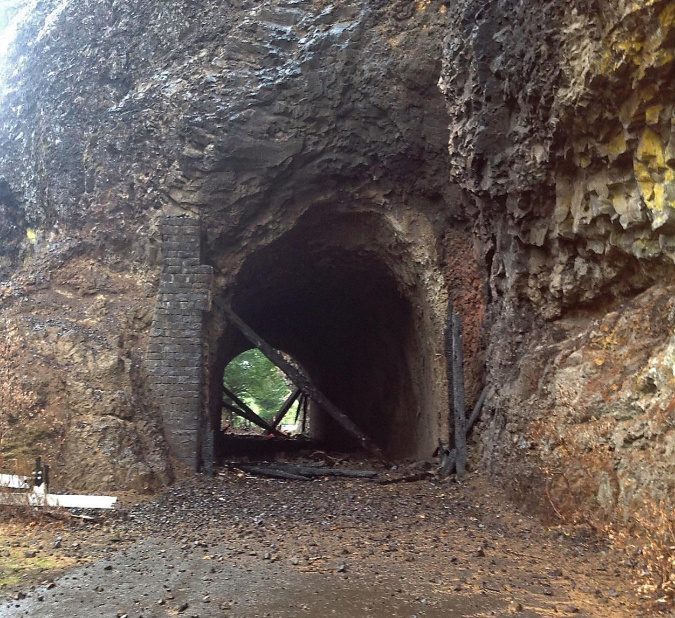
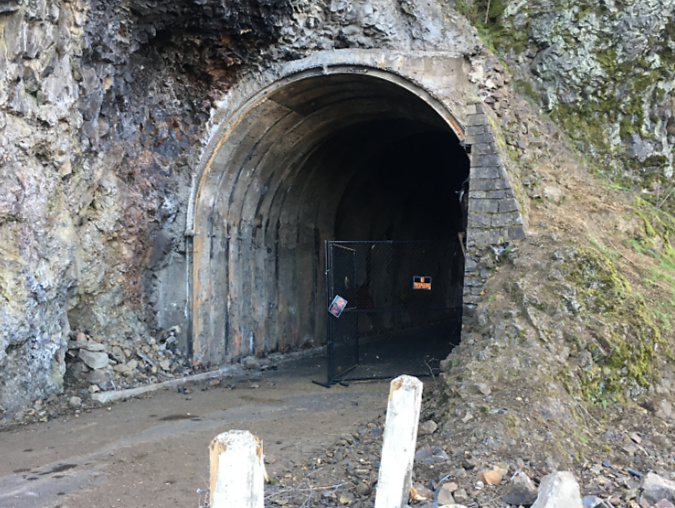
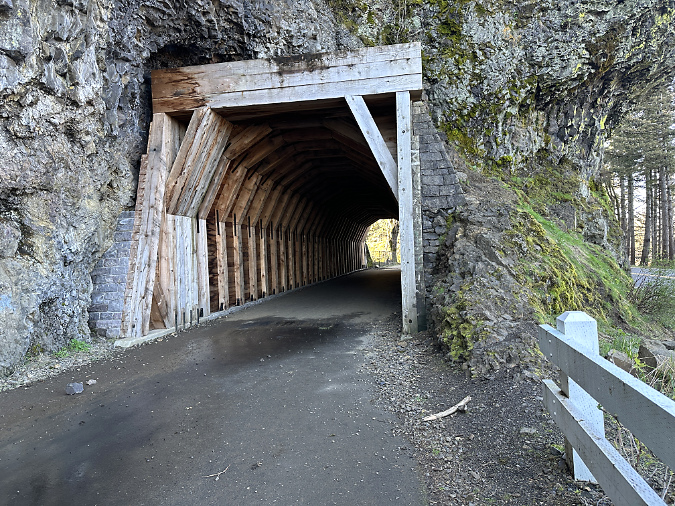
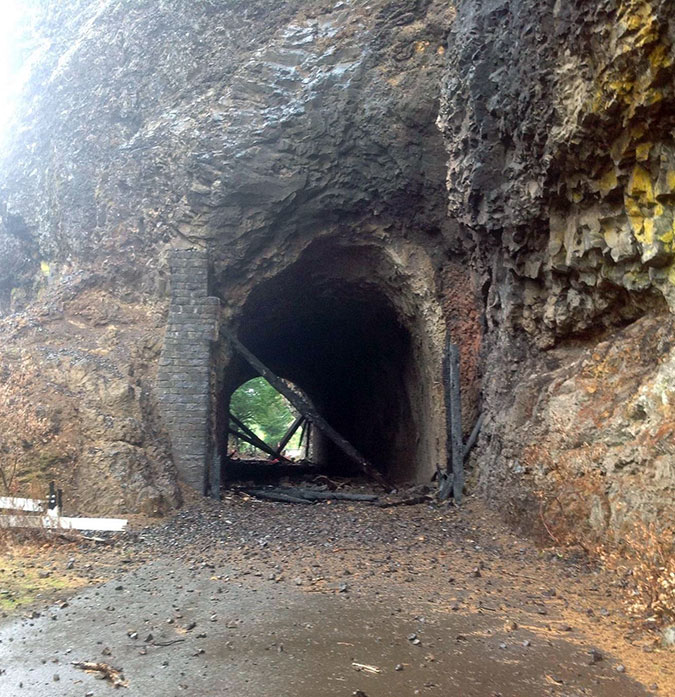
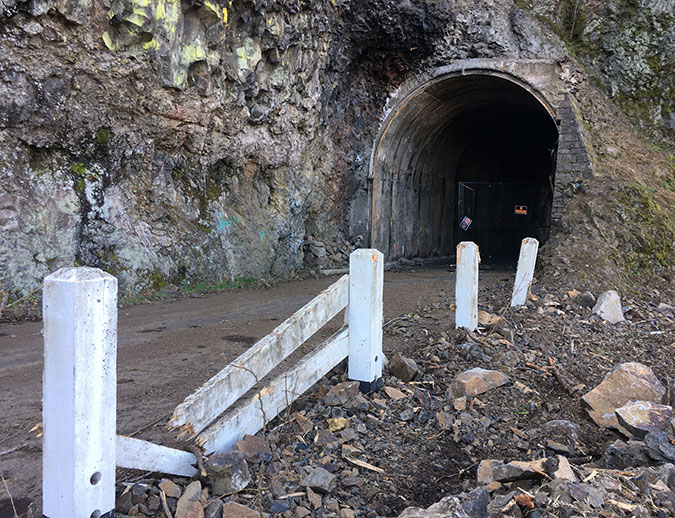
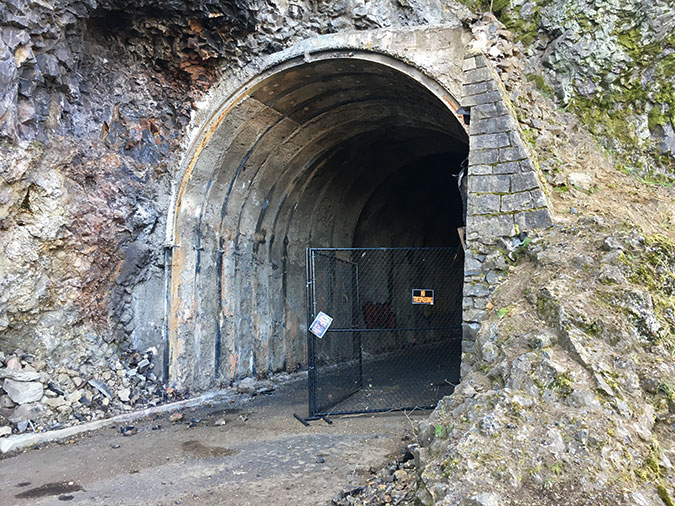
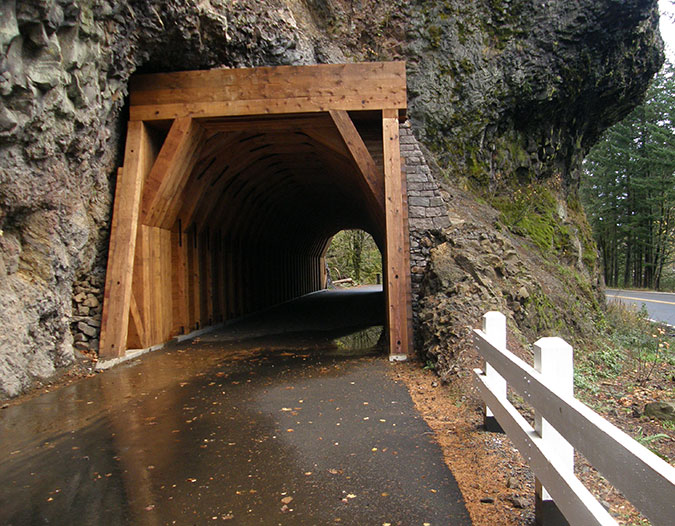
In 2020, ODOT began repairs to the Oneonta Tunnel, once again bringing it back to its original glory with a wood-lined interior. The re-restored tunnel reopened to the public in May 2021.
Oneonta Tunnel cleared and ready for repairs 2020
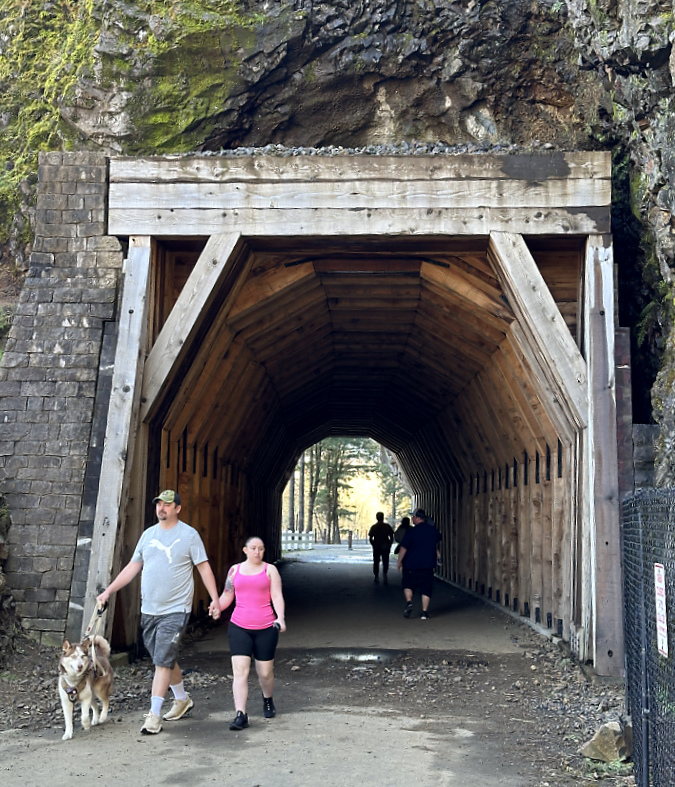
Re-restored the Oneonta Tunnel in 2024
Visitors exploring the reopened Oneonta Tunnel in 2024
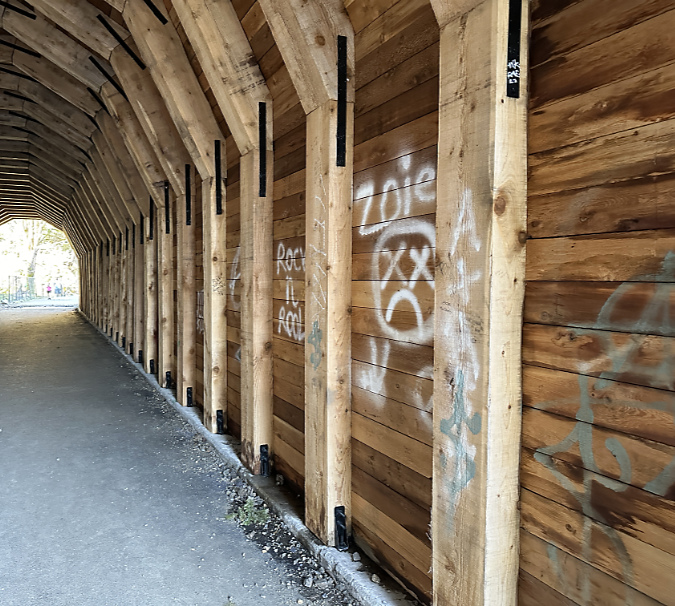
Though the Oneonta Gorge flip-flop crowds are no longer here, vandalism in the newly reopened tunnel continues, albeit at a more manageable pace. While much of the damage before the fire was from names and messages being carved into the soft wood, most of the new vandalism is in the form of spray paint tagging that bedevils our society pretty much everywhere these days. While frustrating, this damage is somewhat easier to repair – assuming ODOT has the capacity and makes it a priority to do so.
When the agency was drawing up plans for the restoring the tunnel a second time, after the fire, I testified to the steering committee that oversees the Historic Columbia River Highway restoration work to consider gating both ends of the tunnel and having State Parks rangers lock it during off-peak hours. I still think this could dramatically reduce vandalism in the tunnel.
Vandalism in the tunnel continues in 2024, despite the Oneonta Gorge closure
Oneonta Tunnel vandalism in 2024
What’s next for Oneonta Gorge? Mostly, a much-needed break from humanity, at least in the near-term. Hopefully, the Forest Service will opt for a long-term plan that places the ecological health of this place at the forefront, but nature has no timeline for clearing out the logs that are making it impassible right now. Over time, the force of water will win out, but that could be decades from now, perhaps longer.
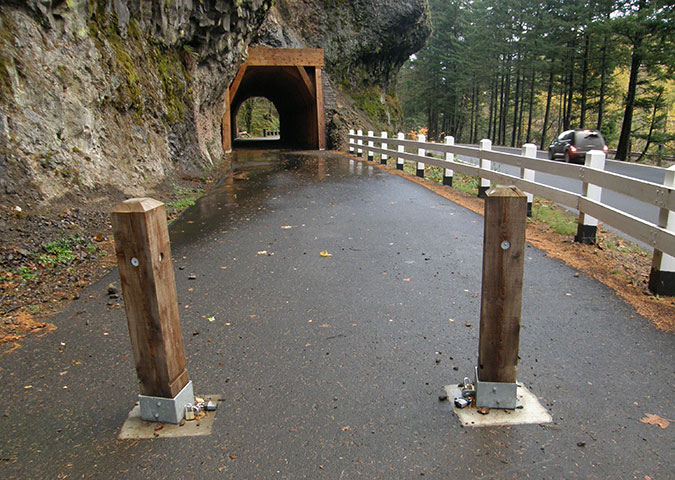
Visitors walking the muddy shoulder to the east portal parking pullout in 2024
I’m also hopeful that ODOT will not only take action to keep pace with vandalism to the tunnel, but also continue to make minor improvements for visitors stopping to explore the tunnel and take in the view of Oneonta Gorge. One that stands out to me when I visits is the surprising lack of even a gravel path to serve the parking pullout near the east tunnel portal (above). A boot path has formed, of course, but I watched several visitors with young kids struggle between the choices of a muddy, narrow boot path and walking adjacent to traffic along the fog line of the eastbound highway lane.
Horsetail-Oneonta wetlands in 2024
If you have followed this blog, you know I’ve posted several articles on Oneonta over the years. This piece surely won’t be the last! For past reads on this magical spot, here are some links:
Let’s Clear the Logjam at Oneonta (2011)
A Second Chance and New Vision for Oneonta? (2020)
If you’d like to hear a recent interview I had with Zach Urness on the future of Oneonta Gorge, you can listen here:
Explore Oregon Podcast: The ballad of beloved Oneonta Gorge
(…and yes, it’s true –I took my wife of nearly 40 years to wade Oneonta Gorge on our first date, way back in September 1981! She didn’t hold it against me…)
________________
Tom Kloster | April 2024