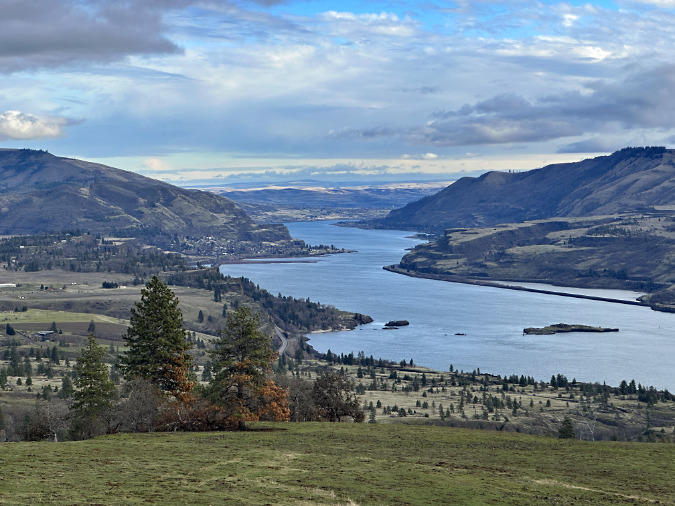
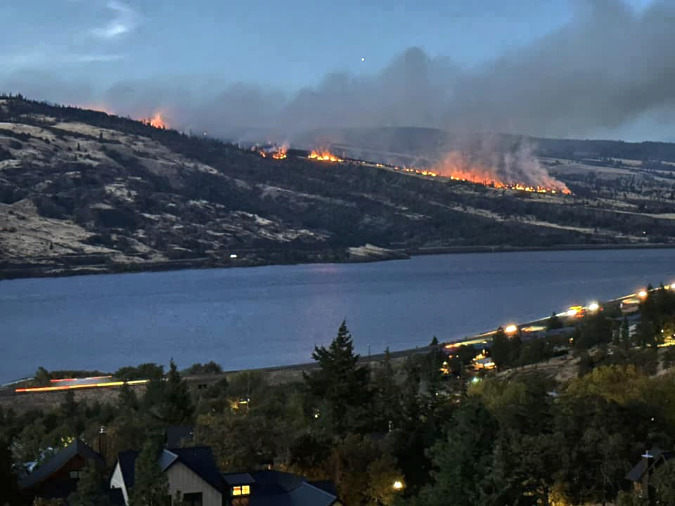
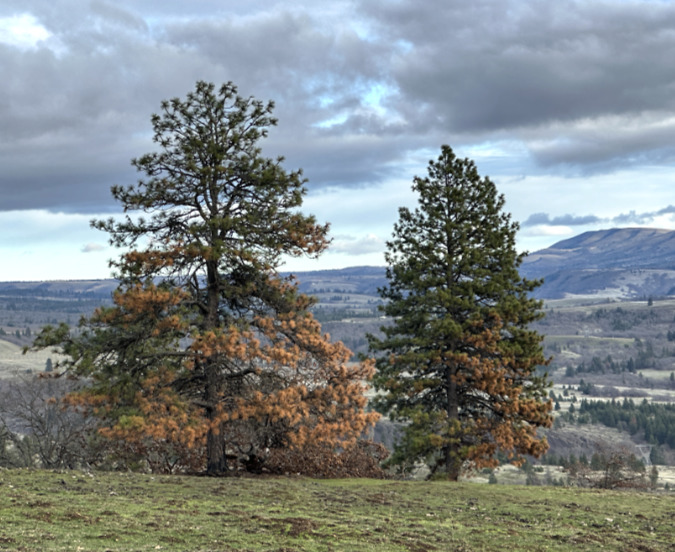
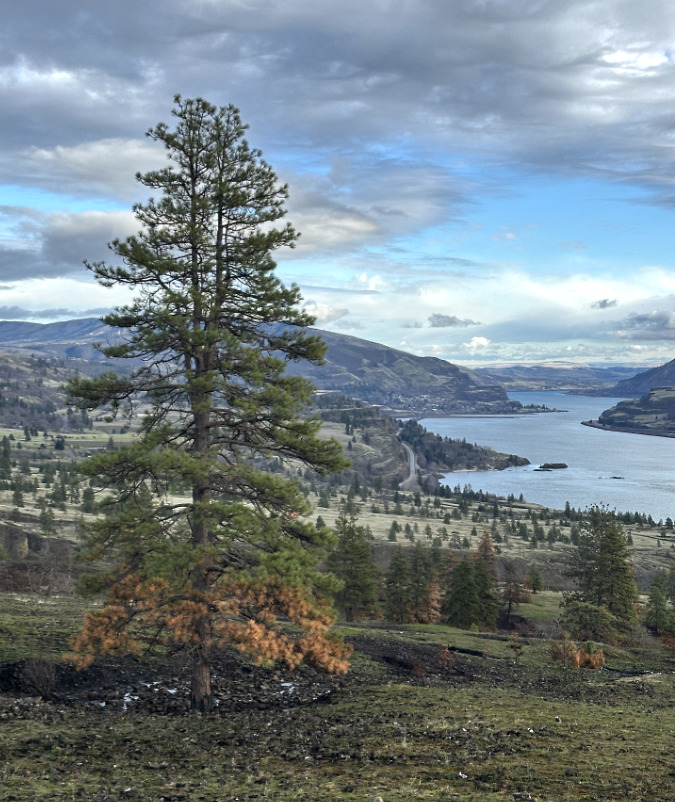
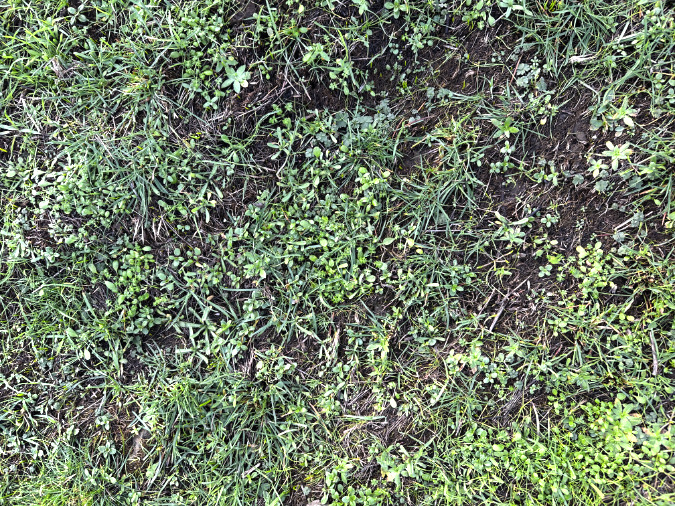
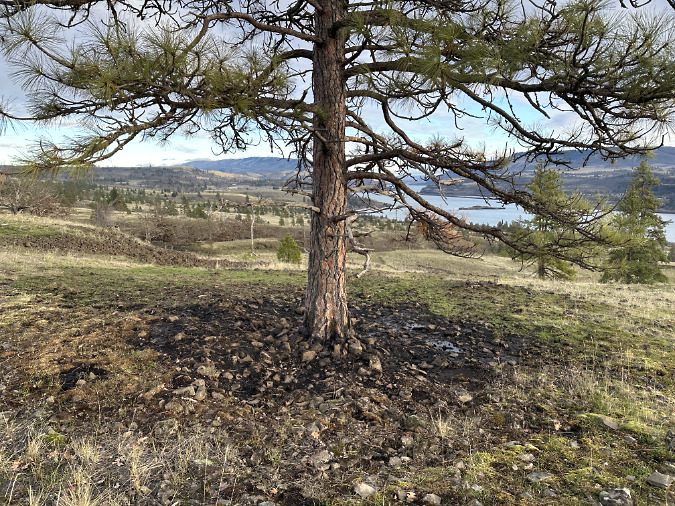
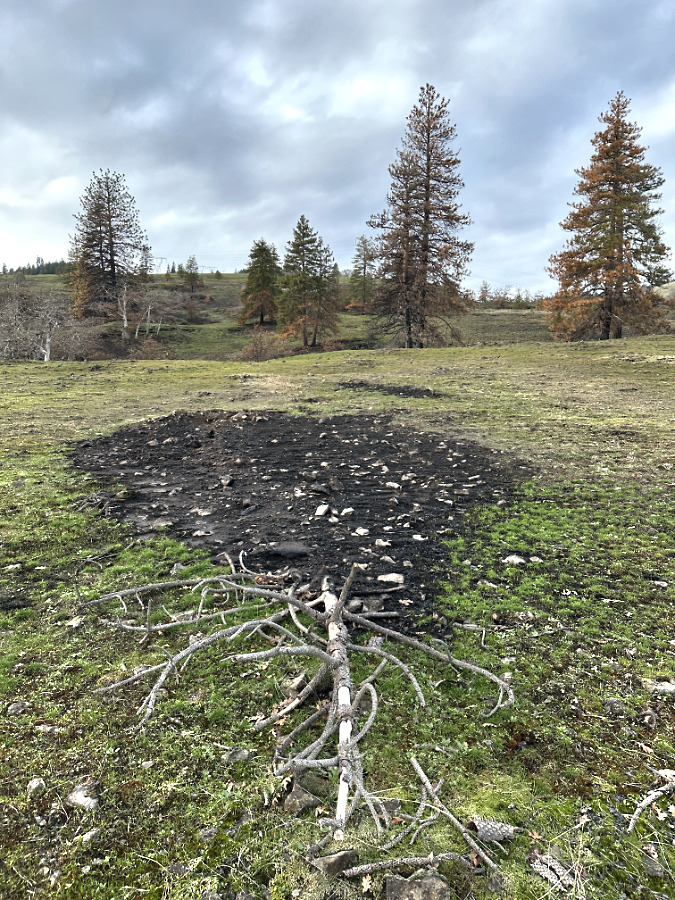
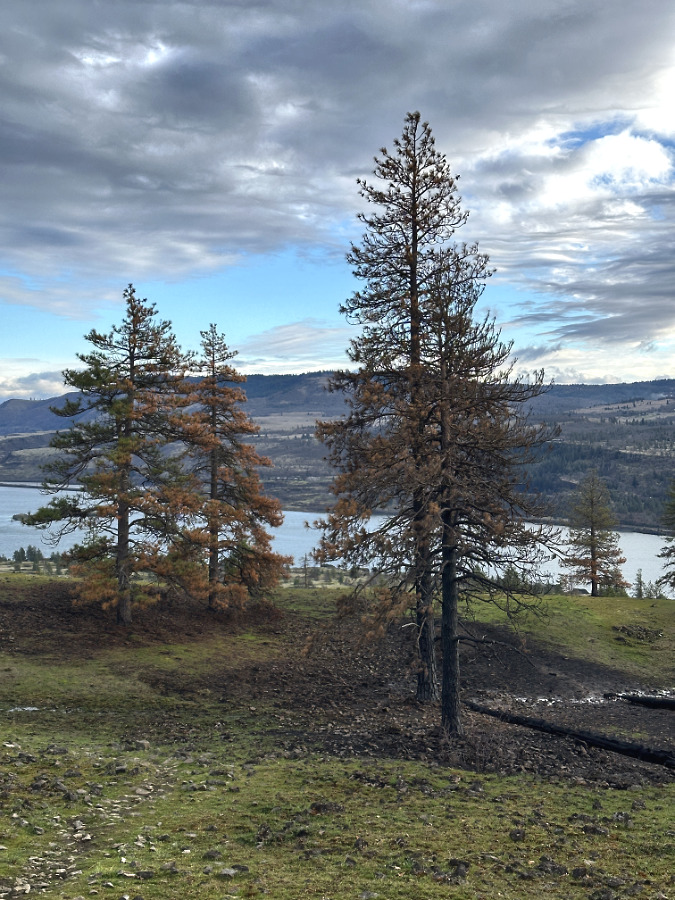
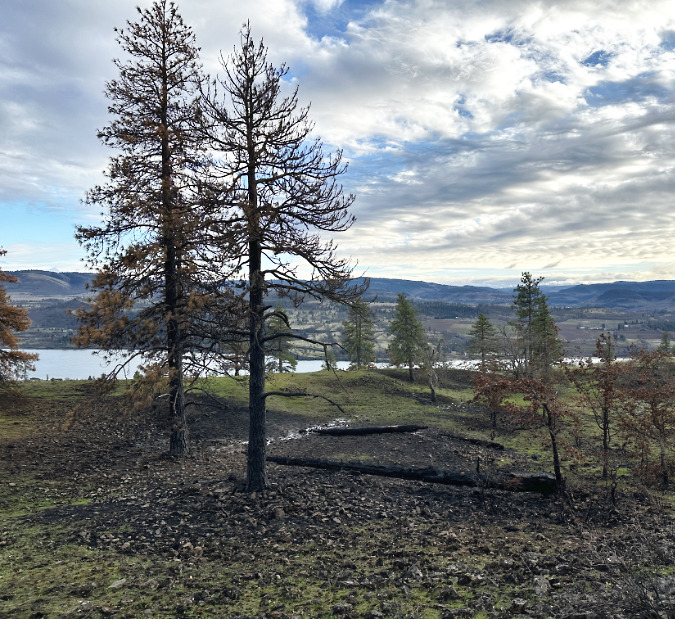
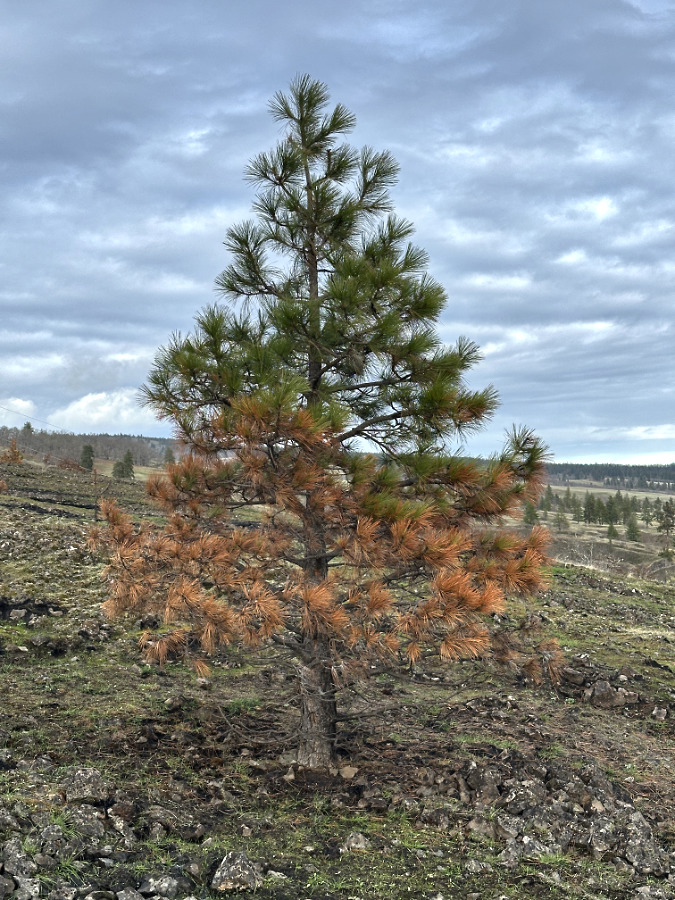
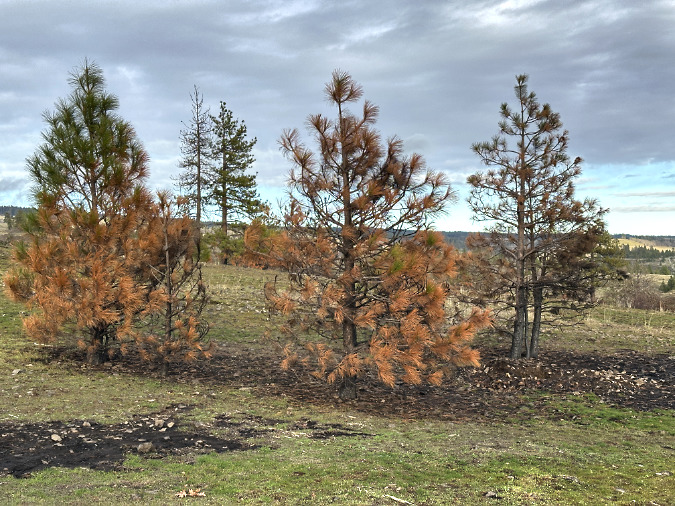
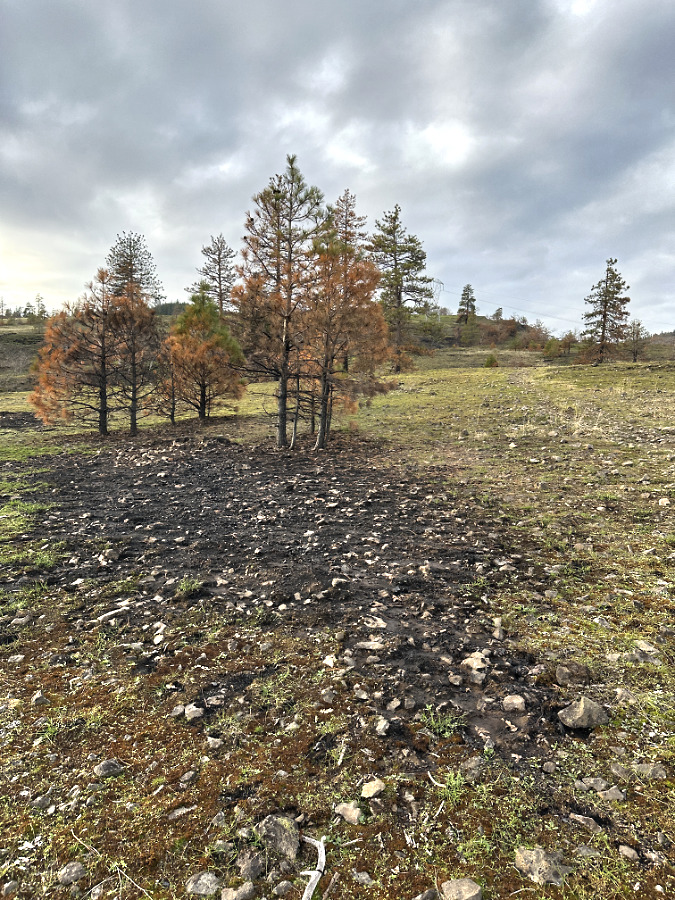
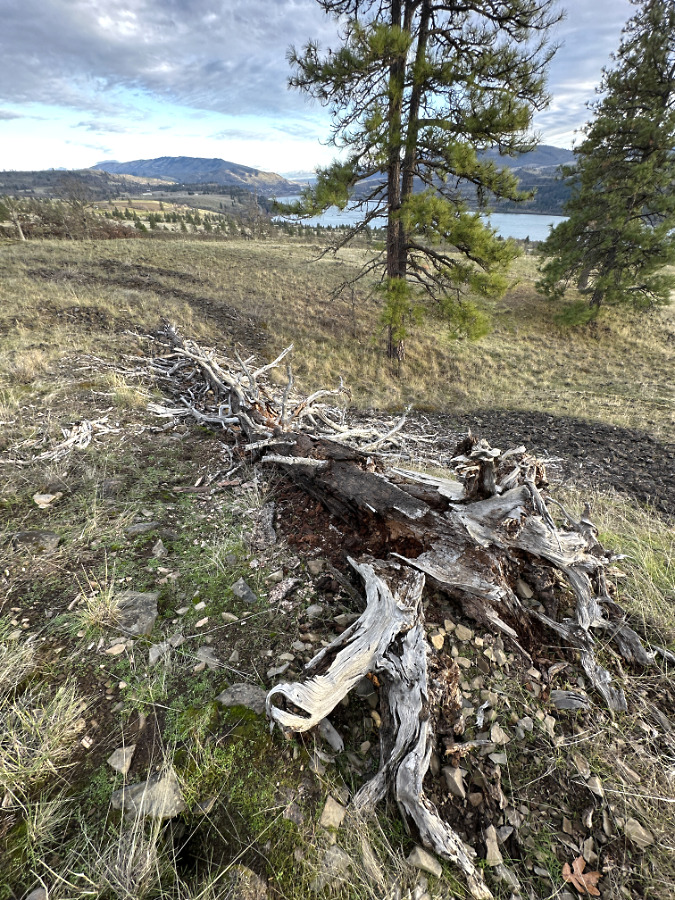
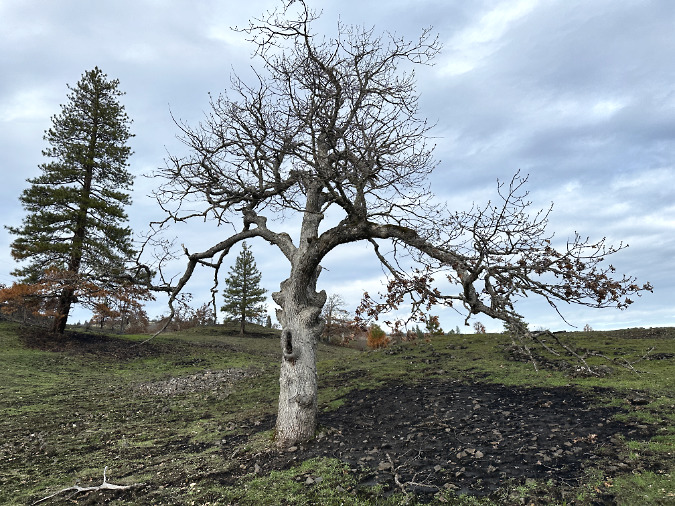
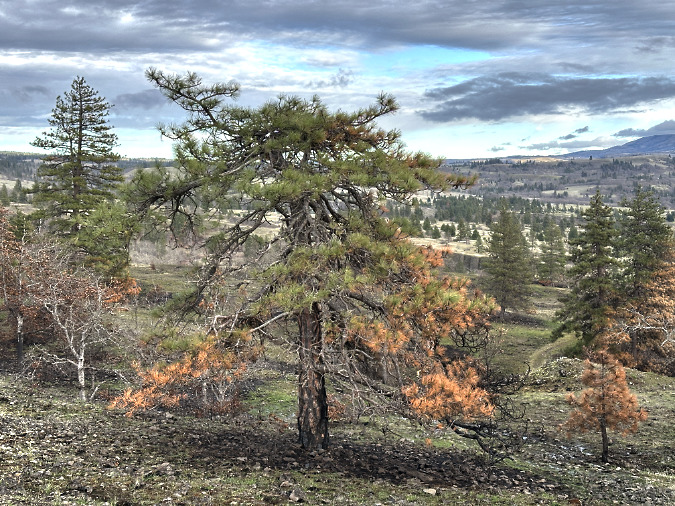
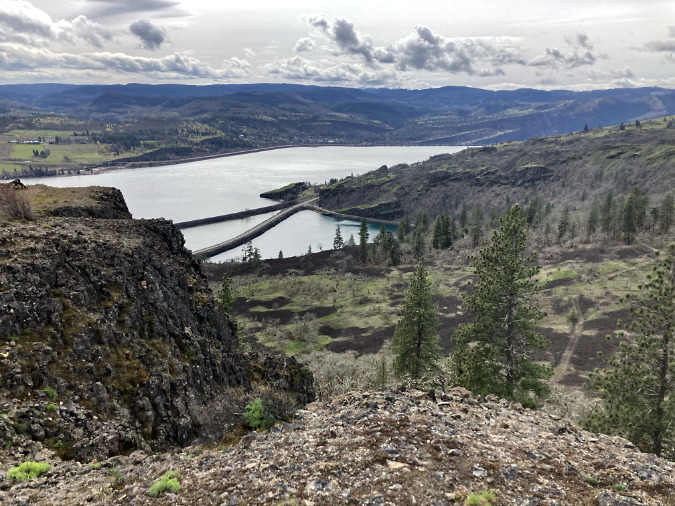
Green regrowth has already returned to the upper meadows at Catherine Creek, just three months after the October 2024 wildfire
Preface: our federal workforce is under unprecedented, highly personal attack by the new administration. The attacks are reckless, cruel and purposely vindictive to the perceived “enemies” of the regime. Many of the newly appointed cabinet officials in the Departments of Interior and Agriculture were specifically selected for their radical, fringe views on the environment and are openly hostile to the very concept of public lands that belong to everyone. We’ll be on defense on this front for the next four years, unfortunately.
Like many articles posted on the blog, I’ve shared my views in this piece on how our public lands at Catherine Creek might be managed in the future. At this moment in our history, however, I also want to open with my unequivocal support for the federal workers who have devoted their careers to caring for our public lands. Over the past three weeks, I’ve seen them proudly and professionally continue to do their work, despite the hostility and mockery of their commitment to public service from the new administration.
U.S. Forest Service workers conduct a controlled burn in Ponderosa country (photo: Deschutes Collaborative)
We’re at a low point as a country, for sure, but I know that we will outlast this regime. Once they have been removed from power, I also believe we will not only restore what damage has been done, but also thrive in a renewed commitment to our public lands. It does (unfortunately) seem that as a nation, sometimes we don’t know what we’ve got until it’s gone. In the meantime, we’ll need to support our federal workers while they are under siege. We can all do that with kind words when we see them out in the field, helping them care for the land, and by sending our support for public lands to our congressional representative and senators. It really does work.
Thanks for indulging me – and now, on to the secrets of the recent wildfire at Catherine Creek…
____________
The opening photo for this article is from a mid-January ramble through the sprawling western meadows of the Catherine Creek savannah, located in the eastern Columbia Gorge near the small town of Lyle. Just three months after a fire swept through the area, only the singed lower limbs on the Ponderosa Pine grove in the distance provide a hint to what unfolded here.
Last October, a wildfire at Catherine Creek was sparked by a prescribed burn that spun out of control, adding to the continuing struggle for public acceptance of controlled burning. The science is definitive, however: controlled fires are the most important tool in restoring forest health and preventing large wildfires in the Western U.S., where our forests are suffering the effects of more than a century of aggressive fire suppression.
While there is plenty to talk about (and learn) on living with fire in the West, this article will focus very locally on some surprising effects on the ground of the fire at Catherine Creek. The meadows are already rapidly rebounding from the event, and there are fascinating traces from the fire that help explain why steep meadows and open savannah exist in the eastern Gorge. Toward the end of the article, I’ll also include some tips on how to see this transformation for yourself, close-up.
The fire…
Early stages of the October 2024 fire at Catherine Creek, just after 4 PM, before it swept across the upper meadows (U.S. Forest Service)
The fire at Catherine Creek was officially named the “Top of the World Fire”. For simplicity, I will simply refer to it as the Catherine Creek fire in this article. The wildfire began at about 4 PM on Monday, October 14, 2024, when unexpected winds lifted embers beyond the boundaries of a controlled burn the Forest Service had been lit that morning.
Once the wildfire was ignited, it quickly spread east and downhill, across the open grassland savannah of Catherine Creek and toward Highway 14. As it grew, more than a hundred firefighters used air tankers, fire trucks and bulldozers to contain the wildfire over the next few days, finally achieving containment by the end of the week.
Late afternoon view of the fire from across the river as it moved into the savannah (Facebook/Susan Garrett Crowley)
Residents of the town of Mosier, located across the Columbia River, had a front row seat to the event. Their images of the fire soon showed up on social media, along with frustration and anger toward the Forest Service for conducting a controlled burn in windy conditions. While these burns are carefully planned with local conditions in mind (including soil moisture, air temperature, humidity and wind speeds), fire can still escape the controlled area, even when all of these variables for a safe burn are met. After all, fire cannot always be controlled in any setting, even with the best of our modern-day technology at hand.
The Forest Service estimates that about 4,500 prescribed burns are conducted across the country each year, covering some 1.3 million acres across the National Forest System. For comparison, that’s roughly equivalent to the entirety of Mount Hood National Forest being treated each year. This might be a surprise to some, given the continued controversy surrounding the practice, but the Forest Service argues that nearly all prescribed fires – 99.8 percent, according to the agency — are carried out as planned.
By early evening the fire had progressed nearly to Highway 14 (Facebook/Mark Paine)
The future of our Western forests looks very challenging for the Forest Service and other land managers. More than a century of accumulated forest debris, an overgrown understory of brush and thickets of unhealthy trees in overplanted clearcuts have created a tinderbox for public land agencies to contend with.
The accelerating effects of climate change will make their job ever more complex as our public land agencies race to reduce the risks of large-scale wildfires with controlled burns, meanwhile continually evolving the practice to somehow achieve the near-perfect success rate needed to maintain public support. Add an ever-growing number of homes being built in the forest margins (often called the wildland-urban interface), and it is hard to imagine that we won’t see future controlled burns escape their planned boundaries.
A closer look…
The effects of fire suppression since the early 1900s are especially pronounced on the east slopes of the Cascades. Here, the forests are dominated by fire-dependent conifers like Ponderosa Pine and Western Larch, but these species have been choked out across much of their habitat by unchecked growth of true firs and other fire-vulnerable species that are crowding east side forests today.
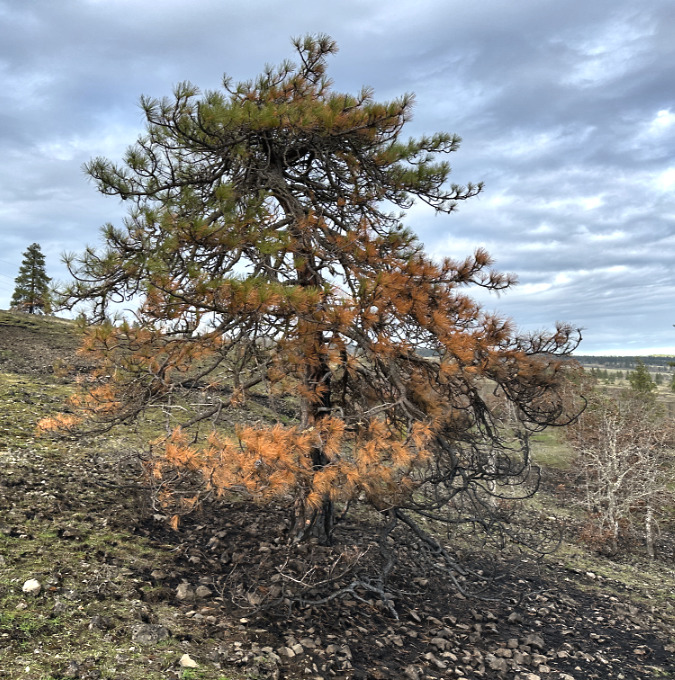
Scorched lower limbs on these Ponderosa Pine are the mark of a beneficial, mostly low-intensity savannah fire
The comparatively dry climate of east-side forests also means more accumulation of dead forest debris that would quickly be covered in moss and succumb to decay on the wet, western slopes of the mountains. This is why fire is so important as part of the east side ecosystem, and why species like Ponderosa Pine have evolved to thrive with fire, not despite it.
The burn scars at Catherine Creek provide a perfect living laboratory to see the beneficial effects of wildfire, firsthand and in real-time. While I’ve tracked the 2011 Dollar Lake Fire on Mount Hood and the 2017 Eagle Creek Fire in this blog to learn from the recovery in those respective ecosystems, the fire at Catherine Creek provides some new insights into the role of fire in the eastern Gorge savannah.
The first thing I noticed on my recent visit were the singed lower limbs on all of the Ponderosa Pine trees that survived the fire. These trees are known for their thick, fire-resistant bark, and in this case, the fire was cool enough to burn just the lower limbs on many of the trees. Most of the large trees here survived because the fire didn’t reach up into their crowns. This is known as “crowning” and something that is usually fatal to a big conifer. The recent fires on Mount Hood and in the Eagle Creek Fire experienced hundreds of acres of crown fires, where the entire forest was killed.
Scorched lower limbs are a good thing for this Ponderosa Pine, as losing these branches will protect it from crown fires in future events
The fact that many of the large Ponderosa Pine even had green limbs all the way to the ground is evidence that a significant fire hasn’t swept through here for some time. Most of the singed limbs on these trees have likely been killed and will eventually fall from the trees. In the near term, they have lost some of the green canopy needed to help the trees survive, but recovering over the long term, they will also become more fire resilient, with their lowest limbs much higher on the tree, and thus out of reach for moderate fires like this one.
The suddenly bright green surface of the burned savannah meadows also has a story to tell. This isn’t simply grass, but also an infinite number of seedlings exploding from the cleared soil, even during the cold winter months. It’s hard to know what species these will mature into this spring, but it’s a fair bet that the wildflowers this area is known for will be even more spectacular in coming years.
Some grass is sprouting in the burned meadows, but also a lot of tiny wildflower seedlings just three months after the fire
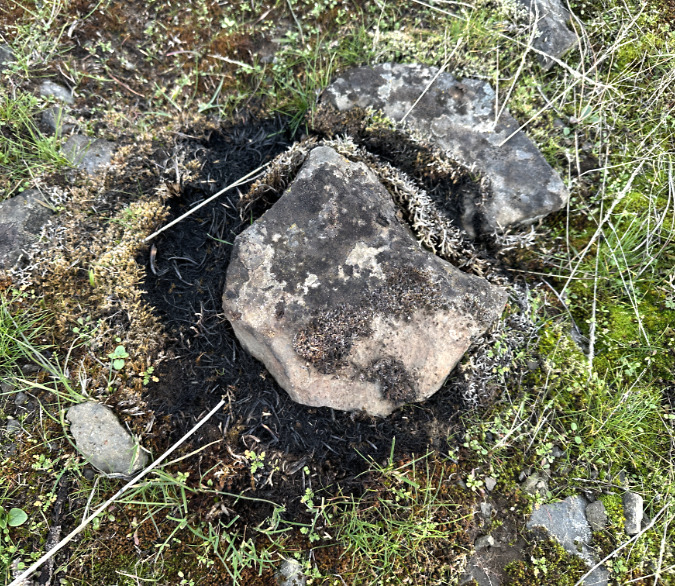
Another surprising story from the fire is how rocks and rocky areas intensified the effects of the flames on vegetation. Throughout the burn, you can find rocks that were superheated by the fire, then stayed hot relative to the surrounding soil after the flames had passed, completely killing vegetation in a ring around the rock (below). It’s hard to know how this will affect the recovering plant community, but in an ecosystem where fire was once common, it surely must have some role in determining which plants thrive most in rocky areas.
Rocks within the burn intensified the impact of the fire, leaving scorched rings like this where vegetation was completely killed
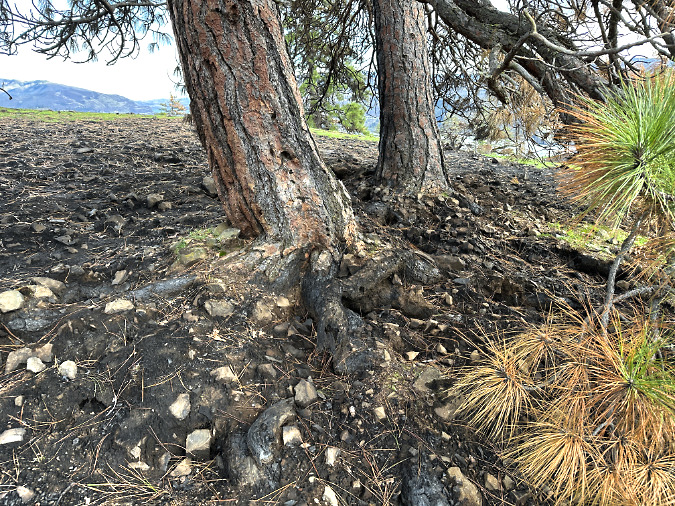
The dripline beneath Ponderosa Pine trees also proved to be a surprising hot spot, with vegetation and sometimes even the duff layer completely burned away. This seems to have resulted mostly from an over-accumulation of wood debris and a blanket of dried pine needles that simply burned hotter and longer during the event. These burn rings underscore the importance of restoring fire to this ecosystem, and not allowing wood debris to build up under these trees to a level where they cannot survive when fire returns.
The charred burn ring under this Ponderosa Pine was less extensive due to the tree’s relative youth, with less dry fuel accumulation to intensify the burn
The charred ring under this part of large Ponderosa Pine is more extensive, burning down to bare rock and mineral soil, due to the larger supply of dry fuel that had accumulated here over many years
One of the most fascinating stories the burn scars can tell us is how downed trees across the savannah landscape affected the intensity of the burn and put nearby, living trees at risk. The blackened swath adjacent to the pair of large Ponderosas shown below marks where a fallen tree burned hotter and much longer than the overall fire, scorching the standing trees halfway up their canopy. These trees will likely survive, but the recovery of the tree on the right will be slower as it struggles to rebuild its living canopy.
A downed tree that left the charred scar shown in this view burned long and hot enough to scorch branches halfway up these nearby Ponderosa Pine
This view (below) of a downed tree scar is typical of dozens across the burned savannah of the Catherine Creek fire. This view is looking from the base of what was once a fallen tree, with a prominent hole in the ground and upturned soil and rocks in the foreground. These mark where tree roots had pulled this material from the ground when the tree originally fell, but are now burned away, leaving only the pile of soil and rock.
Burn scars from downed trees like this are found across much of the savannah area of the Catherine Creek fire, with the trees almost completely reduced to ashes that have since washed away during winter rainstorms. This view from the base of the tree shows the characteristic hole and upturned soil left by the root ball that has since been burned away
This next image (below) is the reverse view of the same fallen tree, now looking from the top. The very tip of this downed tree in the foreground somehow managed to survive the fire, unburned. Even the shape of the fallen tree is apparent in the pyramid-shaped burn scar.
This view of the previous burn scar shows the perspective from the top of the former tree, with only the unburned tip left to tell the story
The bare soil created by these intensively burned patches surely serves a niche in a grassland savannah ecosystem that relies on fire to rejuvenate. I’ll be tracking the recovery of these areas over the next few years to see if certain plants are especially adapted to regenerate in these spots – and conversely, whether these badly burned areas open the door to invasive plants, one of the liabilities of intense fires.
The downed trees and their distinctive burn patterns within the Catherine Creek burn are not an anomaly. While they likely went unnoticed to most who visited this area before the fire, there were hundreds of downed trees spread across the open savannah. This aerial view (below) is just a small area, and yet there were more than 30 downed trees here before the fire (marked by the arrows). All were burned. Their sheer number underscores how the absence of fire has allowed dry debris to accumulate here in recent decades.
There were hundreds of downed trees across the savannah section of the Catherine Creek burn before the fire, mostly unnoticed by hikers traveling through. The arrows mark each blowdown
[click here for a larger view]
Another takeaway from the aerial sample is the uniformity in how these trees fell. Nearly all of them point eastward, revealing the predominant winds from the west in this part of the Gorge – especially in the winter, when soils are saturated and storms are frequent and often powerful.
Surprisingly, some of the big Ponderosa Pine that fared most poorly were growing in stands (below). Here, the combination of their accumulated fuel of dried limbs and needle beds around their trunks combined with fallen trees within the stand for a fire too hot for these trees to survive. Their low canopy – a product of not having fire present until now – also made them vulnerable to the hotter burning that happened here.
These trees help tell the story of why Ponderosa Pine are more often solitary trees within the savannah ecosystem. Not only do they have less competition from other trees for water and nutrients, they are also less vulnerable to spot fires from accumulated debris and fallen trees.
Growing in groves usually helps trees survive by protecting them from wind, but here their close proximity meant a combined debris accumulation — including downed trees — that burned hot and long, killing the largest Ponderosa Pine trees in this group
Another look at the same grove shows how several downed trees combined to create a fiery oven that few trees survived
Young Ponderosa Pine in the burned savannah have their own story to tell about the Catherine Creek fire. This tree (below) lost roughly half its green canopy, but the top survived the fire – so far, at least. This suggests that the flames rolled through fairly quickly. The lack of a burn ring also shows that this tree was too young to have accumulated much dried debris beneath its small canopy. With repeated, low-intensity fires, this tree can continue this pattern until its canopy is high enough from the ground to survive fire events fully intact. This is the classic cycle of a mature Ponderosa Pine forest under the natural conditions in which the species evolved.
Even very young trees can benefit from fire by shedding their lower canopy — if they can survive the loss of so many limbs
This grove of young Ponderosa Pine (below) fared worse, but it wasn’t due to their close proximity to one another, or even a combined accumulation of debris that made them vulnerable. Instead, it was their proximity to a very large, downed tree – perhaps their parent – that burned long and hot enough to badly scorch them. Of the group, only the tree on the left seems to have enough living canopy to survive.
This group of young Ponderosa Pine trees might have fared better had they not been growing around a large, downed tree that burned long and hot just to the right
This view of the same grove of small trees shows the burn scar of a large downed tree that sealed their fate was. The wide shape of the burn scar clearly shows that the tree still had many limbs intact that only added to the heat it produced
Though the recovering meadows in the Catherine Creek burn are rapidly concealing the extent of the burn, the edge of the burn zone can be found by surviving blowdowns, like this one (below), just a few feet beyond the burn scars. This ancient downfall also underscores just how long it has been since fire was a force in this ecosystem – this tree has been lying here for decades.
The hundreds of downed trees that burned across the Catherine Creek savannah looked something like this before the fire. The age of this very old tree skeleton shows that beneficial wildfires have been suppressed here for decades
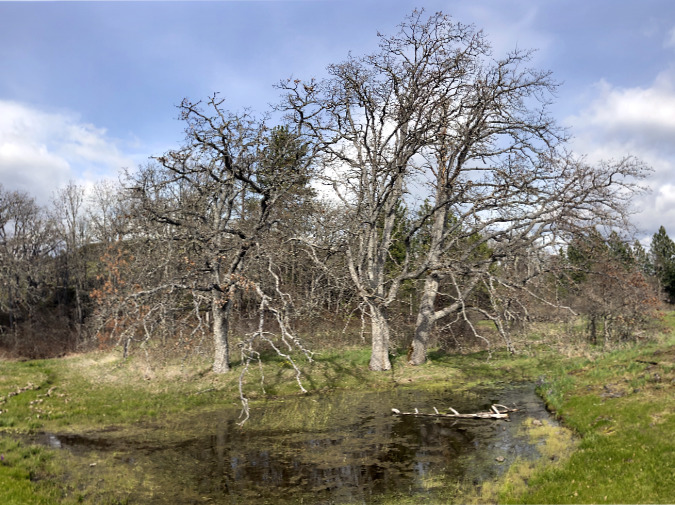
The fire at Catherine Creek didn’t expand far into Oregon White Oak habitat, the other iconic tree species in the eastern Columbia River Gorge. Like Ponderosa Pine, these trees have evolved with fire, and require regular, low-intensity burns for their health. They have deep taproots that help them retain moisture, even during the dry summer season, and corky, protective bark that helps insulate them from low-intensity fire, much like Ponderosa Pine with its thick, orange bark. Oregon White Oak also has less resin in its wood and leaves, making these trees less flammable and prone to crowning than other tree species.
The burn pattern under this Oregon White Oak (below) is much like that of the nearby Ponderosa Pine, and suggest that it, too, had an accumulation of debris that burned hotter and longer, thanks to fire suppression. These oaks also have fire resistant buds, so I’ll be watching to see how well this fire-impacted tree rebounds in spring.
Oregon White Oaks have their own built-in fire resistance, and are adapted to low-intensity brushfires. This tree will likely survive the Catherine Creek burn
Like Ponderosa Pine, our Oregon White Oaks also benefit from having competing brush and understory plants cleared with regular, low intensity fires. In the Willamette Valley, where Oregon White Oak trees grows to be very large, scientists estimate that low-intensity wildfires burned every three to five years prior to white settlement of the Pacific Northwest. Most of these fires were set by indigenous people to maintain the Oak savannah landscape in the valley. I suspect the same was true for the oak groves on the east slopes of the Cascades, as well – especially in the Gorge, where a large indigenous population thrived.
One survivor of the Catherine Creek fire that caught might eye is the humble Ponderosa Pine shown below. It had clearly seen some rough times it its life, losing its top at some point, perhaps to an ice storm, wind or even a lightning strike. The result is an unusually short tree for its age, making it more vulnerable to fire. Still, it appears to have survived the October fire.
This stunted Ponderosa Pine has already suffered adversity in its life on the Catherine Creek savannah. Despite this tree’s humble height and low canopy, it did retain some of its healthy crown after the fire
From the uphill side, this old tree seems to have lost minimal canopy, but viewed from the downhill side (below), the fire had a much greater impact, singeing close to half the canopy. Like most of the Pondersosa Pine, there seems to have been enough accumulation of old limbs and dried pine needles beneath this tree to allow the fire to burn much hotter and longer, and the tree’s low canopy made it still more vulnerable to the heat.
This view of the same stunted Pondera Pine shows a greater impact of the fire on the downhill side of the tree, where accumulated debris likely burned longer and hotter
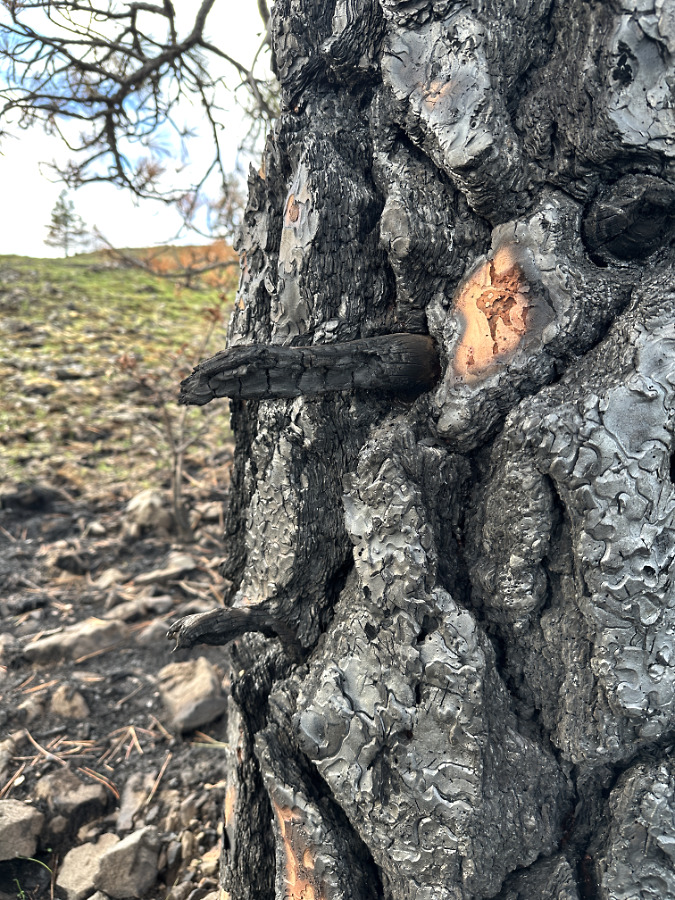
A close look at the trunk on this old, diminutive pine shows just how important Ponderosa bark is to the survival of this species. In a few spots (below) where some of the heavily charred bark has flaked away, the layers of bark underneath are still completely unburned. Therefore, if this tree has enough remaining green canopy to survive the fire, it should have the intact trunk and root system needed to growth and recover. I will be rooting for this survivor!
Ponderosa Pine bark on living trees is remarkably fire-resistant. Just beneath the badly blackened surface, the bark is intact and healthy
It will take years for the full effects of the fire to be known at Catherine Creek, but just three months after the burn, the area is looking both resilient and rejuvenated as open grassland savannah. One hopeful outcome from this event is that it might open the door to future controlled burns on other savannah landscapes in the Gorge in the years to come as we watch and learn from the recovery here.
How to tour the Catherine Creek burn area?
Scorched trail sign in the upper meadows at Catherine Creek
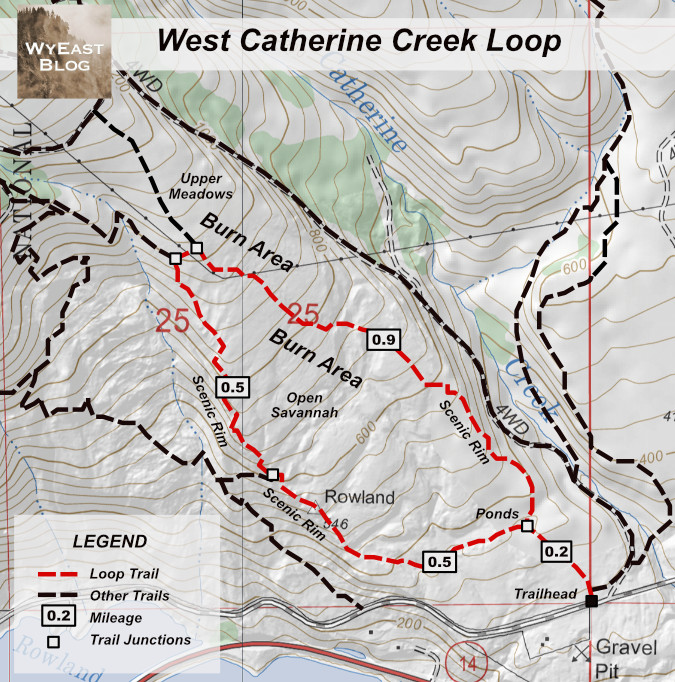
The Catherine Creek trail network can be confusing to explore, as there is both an abundance of trails and a dearth of trail signage! This loop takes you through some of the finest scenery and provides a close look at the 2024 burn recovery, though none of the trail junctions are signed. The loop shown in red works best when hiked clockwise, climbing about 800 feet in elevation in the first mile through mostly open savannah, then dropping the same distance in the remaining 1.3 miles, along the rugged Rowland Wall.
[click here for a large, printable version of this map]
While the mileage is relatively modest, the return loop along the rim is rocky, so an option for the less sure-footed is to simply go as far as you feel like on the first leg to the upper meadows, then return the way you came. One important wayfinding tip in the absence of signs is to look for the critical junction at the 0.2 mile mark when you reach a group of seasonal ponds. Watch for a path that heads right, along the ponds, then climbs a slope to begin following a rocky rim on the way to the savannah section.
Ponds at Catherine Creek mark the start of the loop trail route
The junction at the upper end of the loop can also be hard to find when the meadow grass gets tall, but watch for it on the left when you pass under the obvious transmission lines, roughly halfway between two large transmission towers. Be sure to print a copy of the above map to keep in your pocket, too!
The west leg of the loop, along the Rowland Rim escarpment, also provides fascinating views into dozens of pits in the talus slope below that likely served ceremonial or burial purposes for indigenous people who once lived here in very large numbers. On a clear day, Mount Hood is on the horizon, across the Columbia River. In spring, the entire loop is decorated with wildflowers.
The view from the Rowland Wall section of the hiking loop features Mount Hood (among clouds in this photo) and a maze of ceremonial pits in the talus fields, below, left over the centuries by indigenous peoples
You’ll also be sharing the trail with bikes and possibly horses if you’re on foot. Like all of the eastern Columbia River Gorge, this tick, poison oak and rattlesnake country, with the usual considerations.
Enjoy… and please be kind to your federal lands workers!
________________
Tom Kloster • February 2025